How can you call a subflow from Dataweave?
A. Not possible in Mule 4
B. Import function
C. Lookup function
D. Include function
Explanation:
This is a trick question.
You can call only flows from DataWeave using lookup function. Note that lookup function does not support calling subflows.
A subflow needs a parent context to inherit behaviors from such as exception handling, which a flow does not need Hence correct answer is Not possible in Mule 4
What is the main purpose of flow designer in Design Center?
A. To design and develop fully functional Mule applications in a hosted development environment
B. To design API RAML files in a graphical way
C. To design and mock Mule application templates that must be implemented using Anypoint Studio
D. To define API lifecycle management in a graphical way
Explanation: Its primary function is to design and develop fully functional Mule applications in a hosted development environment.
Refer to the exhibit.
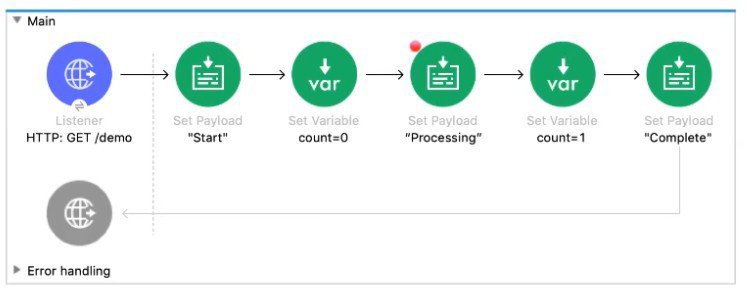
The Mule application Is debugged in Any point Studio and stops at the breakpoint What is the value of the payload displayed In the debugger at this breakpoint?
A. 0
B. "Processing"
C. "Start"
D. Complete"
Refer to the exhibits.
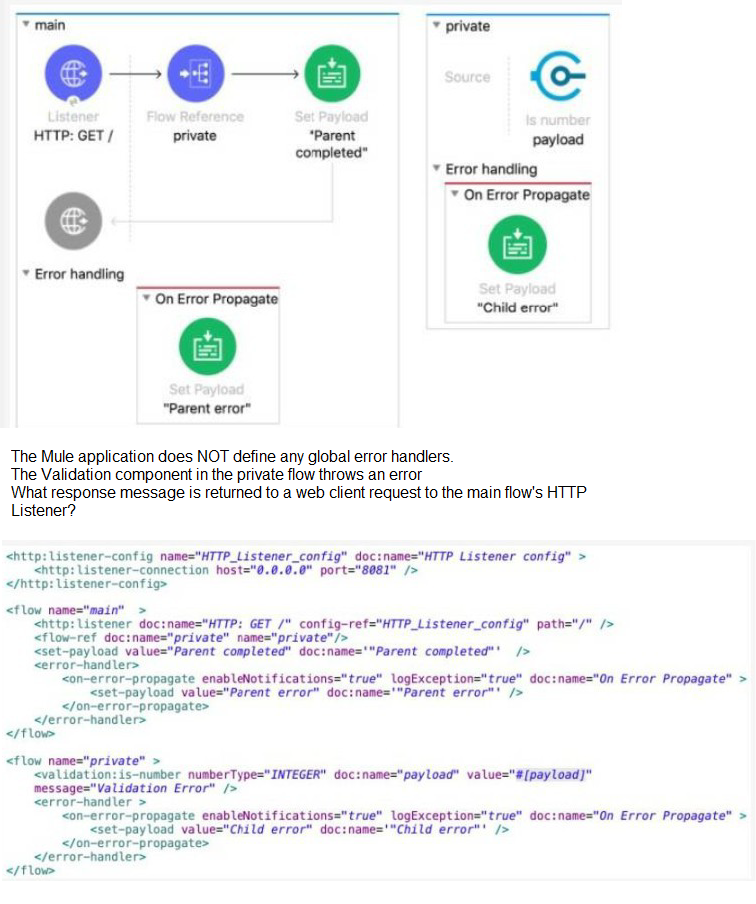
A. ''Child error"
B. "Parent error"
C. "Validation Error"
D. "Parent completed"
Following Mulesoft's recommended API-led connectivity approach , an organization has created an application network. The organization now needs to create API's to transform , orchestrate and aggregate the data provided by the other API's in the application network. This API should be flexible enought ot handle the data from additional API's in future.
According to Mulesoft's recommended API-led connectivity approach , what is the best layer for this new API?
A. Process layer
B. System layer
C. Experience layer
D. Data layer
Explanation:
Correct answer is process layer as all the orchestration and transformation logic should be
in process layer as per Mulesoft's recommended approach for API led connectivity.
API-led connectivity is a methodical way to connect data to applications through reusable and purposeful APIs. These APIs are developed to play a specific role – unlocking data from systems, composing data into processes, or delivering an experience.
What are the APIs that enable API-led connectivity?
API-led connectivity provides an approach for connecting and exposing assets. With this approach, rather than connecting things point-to-point, every asset becomes a managed API – a modern API, which makes it discoverable through self-service without losing control.
The APIs used in an API-led approach to connectivity fall into three categories:
System APIs – these usually access the core systems of record and provide a means of insulating the user from the complexity or any changes to the underlying systems. Once built, many users, can access data without any need to learn the underlying systems and can reuse these APIs in multiple projects.
Process APIs – These APIs interact with and shape data within a single system or across systems (breaking down data silos) and are created here without a dependence on the source systems from which that data originates, as well as the target channels through which that data is delivered.
Experience APIs – Experience APIs are the means by which data can be reconfigured so that it is most easily consumed by its intended audience, all from a common data source, rather than setting up separate point-to-point integrations for each channel. An Experience API is usually created with API-first design principles where the API is designed for the specific user experience in mind.
Refer to the exhibits.
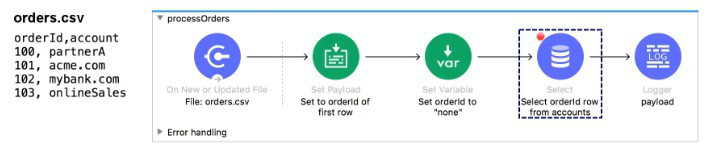
The orders.csv file is read, then processed to look up the orders in a database. The Mule application is debugged in Any point Studio and stops at the breakpoint.
What is the payload shown in the debugger at this breakpoint?
A. "none"
B. The entire CSV file
C. The database response
D. 100
What is the correct syntax to define and call a function in Database?

A. Option A
B. Option B
C. Option C
D. Option D
Explanation:
Keyword to ad function in Dataweave transformation is fun. Hence option 2 and 4 are invalid. Also parameters needs to be passed exactly in same order as defined in function definition. Hence correct answer is'
fun addKV( object: Object, key: String, value: Any) =
object ++ {(key):(value)}
---
addKV ( {"hello': "world"}, "hola", "mundo" )
MuleSoft Documentation Reference : https://docs.mulesoft.com/mule- runtime/4.3/dataweave-functions
DataWeave Function Definition Syntax
To define a function in DataWeave use the following syntax:
fun myFunction(param1, param2, ...) = The fun keyword starts the definition of a function. myFunction is the name you define for the function.
Function names must be valid identifiers.
(param1, param2, … , paramn) represents the parameters that your function accepts. You can specify from zero to any number of parameters, separated by commas (,) and enclosed in parentheses.
The = sign marks the beginning of the code block to execute when the function is called.
represents the actual code that you define for your function.
An API specification is designed using RAML. What is the next step to create a REST Connector from this API specification?
A. Download the API specification and build the interface using APIkit
B. Publish the API specification to Any point Exchange
C. Implement the API specification using flow designer in Design Center
D. Add the specification to a Mule project's src/main/resources/api folder
Explanation: API Exchange creates REST conenctor automtaically once API is published. Hence correct answer is Publish the API specification to Any point Exchange
Refer to the exhibits.
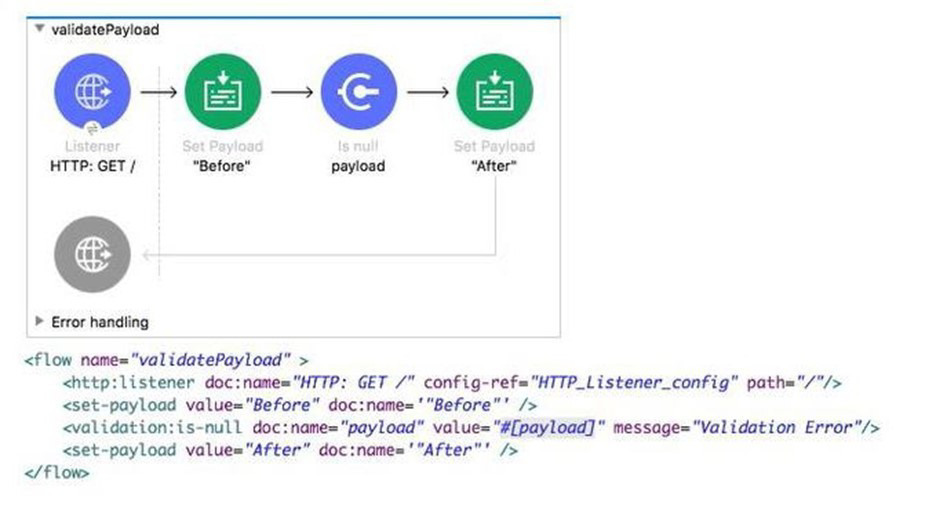
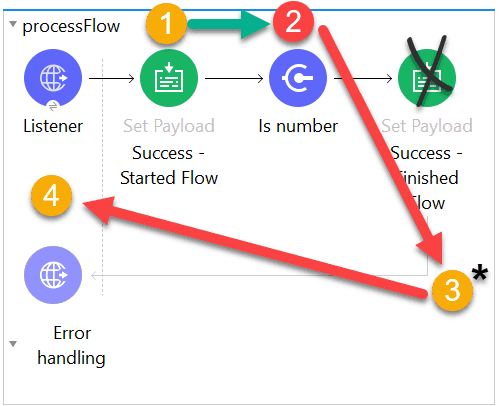
What is the response when a client submits a request to http://localhost:8081?
A. After
B. null
C. Before
D. Validation error
Explanation:
Here’s specifically what is happening here:
1) Payload is successfully set to “Before”
2) Is null validation is used which will pass the message only if payload is null. In this case as payload is not null, it creates an Error Object. Flow execution stops
#[error.description] = “Validation error”
3) Because no error handler is defined, the Mule default error handler handles the error
4) “Validation error” is the error message returned to the requestor in the body of the HTTP request with HTTP Status Code: 500
Reference diagram:
By default, what happens to a file after it is read using an FTP connector Read operation?
A. The file is deleted from the folder
B. The file is moved to a different folder
C. The file stays in the same folder unchanged
D. The file is renamed in the same folder
Explanation: File is not updated when FTP read operations is performed.
What is the output of Dataweave Map operator?
A. Map
B. Object
C. String
D. Array
Explanation:
Returns an array that is the result of applying a transformation function (lambda) to each of the elements.
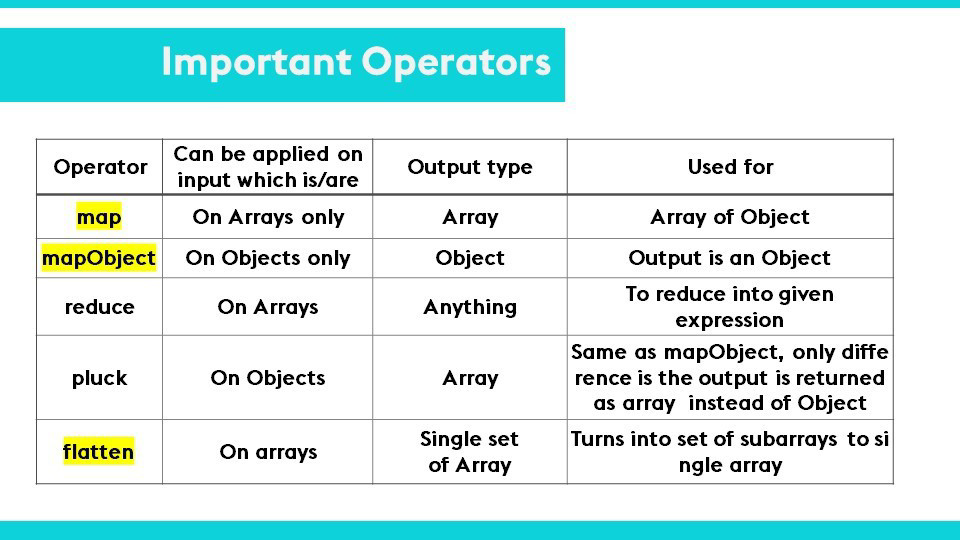
The map operator is a function in Dataweave which iterates over the items in an array and outputs them into a new array. It basically accepts input as a list of items in an array and manipulates the items in the array in order to form a new array as an output.
A web client sends one GET request to the test flow's HTTP Listener, which causes the test flow to call the updateTemp flow After the test flow returns a response, the web client then sends a different GET request to trie getTemp flow's HTTP Listener The test flow is not called a second time.
What response is returned from the request to the getTemp flow's HTTP Listener?
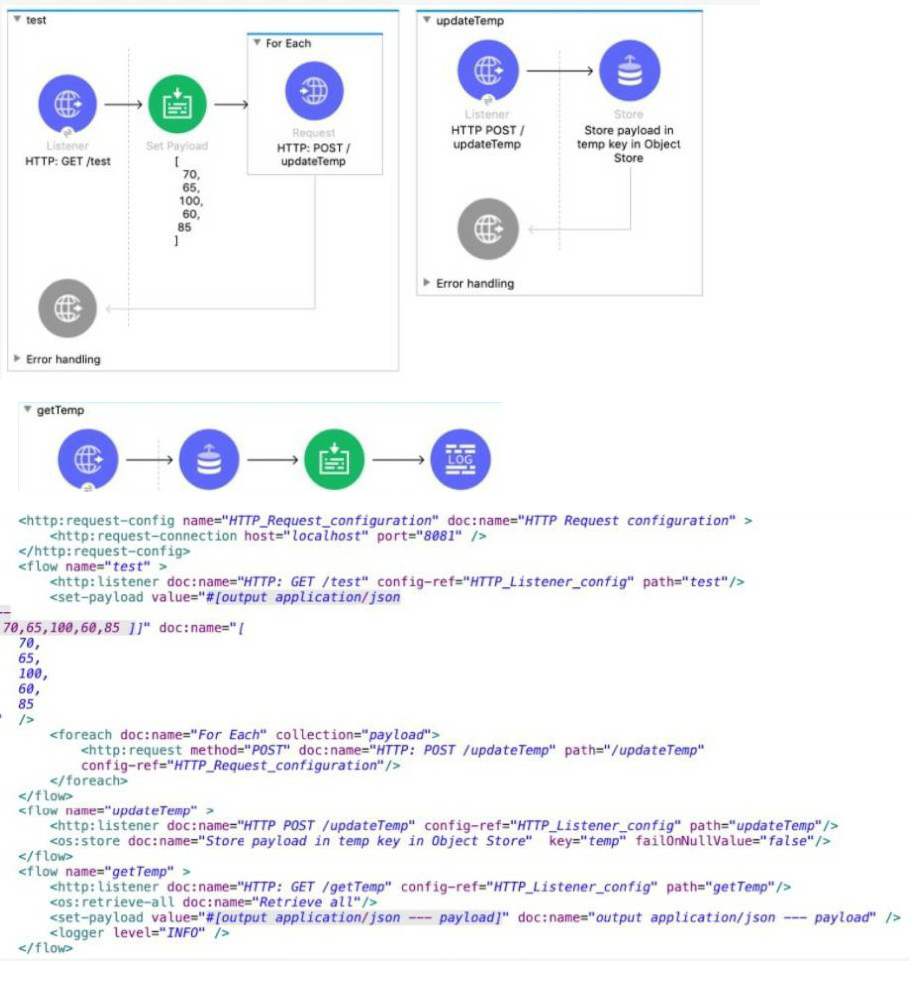

A. Option A
B. Option B
C. Option C
D. Option D
| Page 7 out of 20 Pages |
| Previous |