When using SAML, where does user authentication occur?
A. Splunk generates a SAML assertion that authenticates the user.
B. The Service Provider (SP) decodes the SAML request and authenticates the user.
C. The Identity Provider (IDP) decodes the SAML request and authenticates the user.
D. The Service Provider (SP) generates a SAML assertion that authenticates the user.
Explanation: When using SAML, user authentication occurs at the Identity Provider (IDP). The IDP is a system that verifies the user’s identity and provides a SAML assertion to the Service Provider (SP). The SP is a system that trusts the IDP and grants access to the user based on the SAML assertion. The SAML assertion contains information about the user’s identity, attributes, and authorization level.
A customer has a multisite cluster (two sites, each site in its own data center) and users experiencing a slow response when searches are run on search heads located in either site. The Search Job Inspector shows the delay is being caused by search heads on either site waiting for results to be returned by indexers on the opposing site. The network team has confirmed that there is limited bandwidth available between the two data centers, which are in different geographic locations. Which of the following would be the least expensive and easiest way to improve search performance?
A. Configure site_search_factor to ensure a searchable copy exists in the local site for each search head.
B. Move all indexers and search heads in one of the data centers into the same site.
C. Install a network pipe with more bandwidth between the two data centers.
D. Set the site setting on each indexer in the server.conf clustering stanza to be the same for all indexers regardless of site.
Explanation: The least expensive and easiest way to improve search performance for a multisite cluster with limited bandwidth between sites is to configure site_search_factor to ensure a searchable copy exists in the local site for each search head. This option allows the search heads to use search affinity, which means they will prefer to search the data on their local site, avoiding network traffic across sites. This option also preserves the disaster recovery benefit of multisite clustering, as each site still has a full copy of the data. Therefore, the correct answer is A, configure site_search_factor to ensure a searchable copy exists in the local site for each search head.
Which of the following statements is true, as it pertains to search head clustering (SHC)?
A. SHC is supported on AIX, Linux, and Windows operating systems.
B. Maximum number of nodes for a SHC is 10.
C. SHC members must run on the same hardware specifications.
D. Minimum number of nodes for a SHC is 5.
Explanation: Splunk Data Model Acceleration (DMA) summaries are stored in
summaryHomePath, which is an attribute in the indexes.conf file that specifies the location
of the summary files for data model acceleration. By default, the summaryHomePath is set
to $SPLUNK_DB/
What should be considered when running the following CLI commands with a goal of accelerating an index cluster migration to new hardware?

A. Data ingestion rate
B. Network latency and storage IOPS
C. Distance and location
D. SSL data encryption
Explanation: Network latency is the time it takes for data to travel from one point to
another, and storage IOPS is the number of input/output operations per second. These
factors can affect the performance of the migration and should be taken into account when
planning and executing the migration.
The CLI commands that you have shown in the image are used to adjust the maximum
load that a peer node can handle during bucket replication and rebuilding. These settings
can affect the performance and efficiency of an index cluster migration to new hardware.
Therefore, some of the factors that you should consider when running these commands
are:
Data ingestion rate: The higher the data ingestion rate, the more buckets will be
created and need to be replicated or rebuilt across the cluster. This will increase
the load on the peer nodes and the network bandwidth. You might want to lower
the max_peer_build_load and max_peer_rep_load settings to avoid overloading
the cluster during migration.
Network latency and storage IOPS: The network latency and storage IOPS are
measures of how fast the data can be transferred and stored between the peer
nodes. The lower these values are, the longer it will take for the cluster to replicate
or rebuild buckets. You might want to increase the max_peer_build_load and
max_peer_rep_load settings to speed up the migration process, but not too high
that it causes errors or timeouts.
Distance and location: The distance and location of the peer nodes can also affect
the network latency and bandwidth. If the peer nodes are located in different
geographic regions or data centers, the data transfer might be slower and more
expensive than if they are in the same location. You might want to consider using
site replication factor and site search factor settings to optimize the cluster for
multisite deployment.
SSL data encryption: If you enable SSL data encryption for your cluster, it will add
an extra layer of security for your data, but it will also consume more CPU
resources and network bandwidth. This might slow down the data transfer and
increase the load on the peer nodes. You might want to balance the trade-off
between security and performance when using SSL data encryption.
A customer with a large distributed environment has blacklisted a large lookup from the search bundle to decrease the bundle size using distsearch.conf. After this change, when running searches utilizing the lookup that was blacklisted they see error messages in the Splunk Search UI stating the lookup file does not exist. What can the customer do to resolve the issue?
A. The search needs to be modified to ensure the lookup command specifies parameter local=true.
B. The blacklisted lookup definition stanza needs to be modified to specify setting allow_caching=true.
C. The search needs to be modified to ensure the lookup command specified parameter blacklist=false.
D. The lookup cannot be blacklisted; the change must be reverted.
Explanation: The customer can resolve the issue by modifying the blacklisted lookup definition stanza to specify setting allow_caching=true. This option allows the lookup to be cached on the search head and used for searches, without being included in the search bundle that is distributed to the indexers. This way, the customer can reduce the bundle size and avoid the error messages. Therefore, the correct answer is B, the blacklisted lookup definition stanza needs to be modified to specify setting allow_caching=true.
Consider the search shown below.
What is this search’s intended function?
A. To return all the web_log events from the web index that occur two hours before and after the most recent high severity, denied event found in the firewall index.
B. To find all the denied, high severity events in the firewall index, and use those events to further search for lateral movement within the web index.
C. To return all the web_log events from the web index that occur two hours before and after all high severity, denied events found in the firewall index.
D. To search the firewall index for web logs that have been denied and are of high severity.
The customer has an indexer cluster supporting a wide variety of search needs, including
scheduled search, data model acceleration, and summary indexing. Here is an excerpt
from the cluster mater’s server.conf:
Which strategy represents the minimum and least disruptive change necessary to protect
the searchability of the indexer cluster in case of indexer failure?
A. Enable maintenance mode on the CM to prevent excessive fix-up and bring the failed indexer back online.
B. Leave replication_factor=2, increase search_factor=2 and enable summary_replication.
C. Convert the cluster to multi-site and modify the server.conf to be site_replication_factor=2, site_search_factor=2.
D. Increase replication_factor=3, search_factor=2 to protect the data, and allow there to always be a searchable copy.
Explanation: This is the minimum and least disruptive change necessary to protect the
searchability of the indexer cluster in case of indexer failure, because it ensures that there
are always at least two copies of each bucket in the cluster, one of which is searchable.
This way, if one indexer fails, the cluster can still serve search requests from the remaining
copy. Increasing the replication factor and search factor also improves the cluster’s
resiliency and availability. The other options are incorrect because they either do not protect the searchability of the
cluster, or they require more changes and disruptions to the cluster.
Option A is incorrect
because enabling maintenance mode on the CM does not prevent excessive fix-up, but
rather delays it until maintenance mode is disabled. Maintenance mode also prevents
searches from running on the cluster, which defeats the purpose of protecting searchability.
Option B is incorrect because leaving replication_factor=2 means that there is only one
searchable copy of each bucket in the cluster, which is not enough to protect searchability
in case of indexer failure. Enabling summary_replication does not help with this issue, as it
only applies to summary indexes, not all indexes.
Option C is incorrect because converting the cluster to multi-site requires a lot of changes and disruptions to the cluster, such as
reassigning site attributes to all nodes, reconfiguring network settings, and rebalancing
buckets across sites. It also does not guarantee that there will always be a searchable copy
of each bucket in each site, unless the site replication factor and site search factor are set
accordingly.
When setting up a multisite search head and indexer cluster, which nodes are required to declare site membership?
A. Search head cluster members, deployer, indexers, cluster master
B. Search head cluster members, deployment server, deployer, indexers, cluster master
C. All splunk nodes, including forwarders, must declare site membership
D. Search head cluster members, indexers, cluster master
Explanation: The internal Splunk authentication will take precedence over any external schemes, such as LDAP. This means that if a username exists in both $SPLUNK_HOME/etc/passwd and LDAP, the Splunk platform will attempt to log in the user using the native authentication first. If the authentication fails, and the failure is not due to a nonexistent local account, then the platform will not attempt to use LDAP to log in. If the failure is due to a nonexistent local account, then the Splunk platform will attempt a login using the LDAP authentication scheme.
What is required to setup the HTTP Event Collector (HEC)?
A. Each HEC input requires a unique name but token values can be shared.
B. Each HEC input requires an existing forwarder output group.
C. Each HEC input entry must contain a valid token.
D. Each HEC input requires a Source name field.
Explanation: Each HEC input requires a unique name but token values can be shared. The name is a human-readable identifier for the input that appears in Splunk Web. The name must be unique among all HEC inputs on the same Splunk platform instance. The token value is a string of alphanumeric characters that acts as an identifier and an authentication code for the input. You can use the same token value for multiple inputs, but it is recommended to use different tokens for different data sources or applications.
Consider the scenario where the /var/log directory contains the files secure, messages,
cron, audit. A customer has created the following inputs.conf stanzas in the same Splunk
app in order to attempt to monitor the files secure and messages:
Which file(s) will actually be actively monitored?
A. /var/log/secure
B. /var/log/messages
C. /var/log/messages, /var/log/cron, /var/log/audit, /var/log/secure
D. /var/log/secure, /var/log/messages
Explanation: The inputs.conf stanzas in the image are attempting to monitor the files secure and messages in the /var/log directory. However, the whitelist attribute is set to “messages” and “secure” respectively, which means that only those files will be actively monitored. Therefore, the correct answer is D. /var/log/secure, /var/log/messages.
As a best practice which of the following should be used to ingest data on clustered indexers?
A. Monitoring (via a process), collecting data (modular inputs) from remote systems/applications
B. Modular inputs, HTTP Event Collector (HEC), inputs.conf monitor stanza
C. Actively listening on ports, monitoring (via a process), collecting data from remote systems/applications
D. splunktcp, splunktcp-ssl, HTTP Event Collector (HEC)
Explanation: As a best practice, the following should be used to ingest data on clustered indexers: splunktcp, splunktcp-ssl, HTTP Event Collector (HEC). These are the methods that allow data to be sent to the indexers by forwarders or other data sources, without requiring any configuration on the indexers themselves. The indexers can receive the data on specific ports and index it according to the cluster settings. These methods also support load balancing and encryption of the data. Therefore, the correct answer is D. splunktcp, splunktcp-ssl, HTTP Event Collector (HEC).
A customer has written the following search:
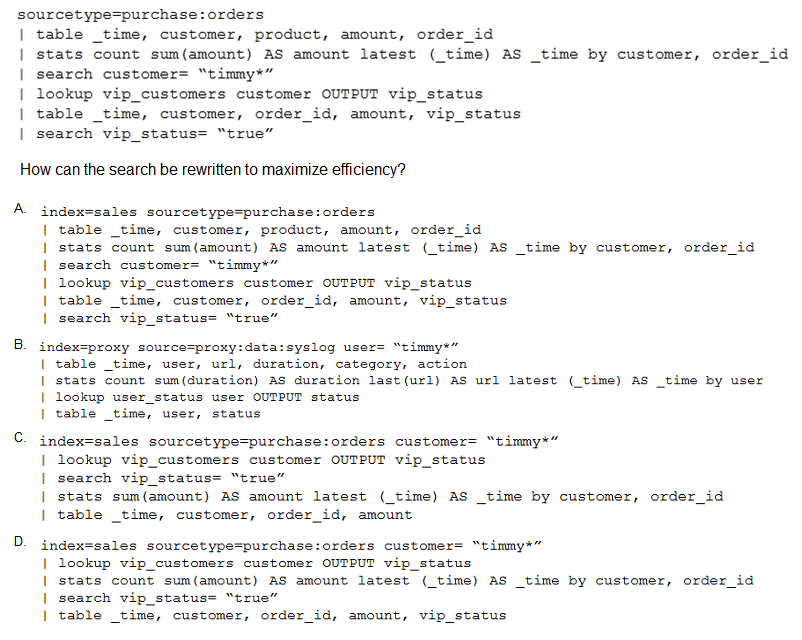
A. Option A
B. Option B
C. Option C
D. Option D
Explanation: The search can be rewritten to maximize efficiency by using the index option. The index option is used to specify the index to search. This option is useful when you have multiple indexes and want to search only one of them. The index option is also useful when you want to search a specific index that is not the default index. The index option can reduce the search time and resource consumption by limiting the scope of the search.
| Page 2 out of 8 Pages |
| Previous |