Which three authentication types can be used to authenticate users? (Choose three.)
A. Local database authentication
B. PingID
C. Kerberos single sign-on
D. GlobalProtect client
E. Cloud authentication service
Explanation:
The three authentication types that can be used to authenticate users are:
A: Local database authentication: This is the authentication type that uses the local
user database on the firewall or Panorama to store and verify user credentials1.
C: Cloud authentication service: This is the authentication type that uses a cloudbased
identity provider, such as Okta, PingOne, or PingFederate, to authenticate
users and provide SAML assertions to the firewall or Panorama2.
E: Kerberos single sign-on: This is the authentication type that uses the Kerberos
protocol to authenticate users who are logged in to a Windows domain and provide
them with seamless access to resources on the firewall or Panorama3.
What type of NAT is required to configure transparent proxy?
A. Source translation with Dynamic IP and Port
B. Destination translation with Static IP
C. Source translation with Static IP
D. Destination translation with Dynamic IP
A firewall engineer creates a NAT rule to translate IP address 1.1.1.10 to 192.168.1.10. The engineer also plans to enable DNS rewrite so that the firewall rewrites the IPv4 address in a DNS response based on the original destination IP address and translated destination IP address configured for the rule. The engineer wants the firewall to rewrite a DNS response of 1.1.1.10 to 192.168.1.10. What should the engineer do to complete the configuration?
A. Create a U-Turn NAT to translate the destination IP address 192.168.1.10 to 1.1.1.10 with the destination port equal to UDP/53.
B. Enable DNS rewrite under the destination address translation in the Translated Packet section of the NAT rule with the direction Forward.
C. Enable DNS rewrite under the destination address translation in the Translated Packet section of the NAT rule with the direction Reverse.
D. Create a U-Turn NAT to translate the destination IP address 1.1.1.10 to 192.168.1.10 with the destination port equal to UDP/53.
Explanation: If the DNS response matches the Original Destination Address in the rule, translate the DNS response using the same translation the rule uses. For example, if the rule translates IP address 1.1.1.10 to 192.168.1.10, the firewall rewrites a DNS response of 1.1.1.10 to 192.168.1.10.
Exhibit.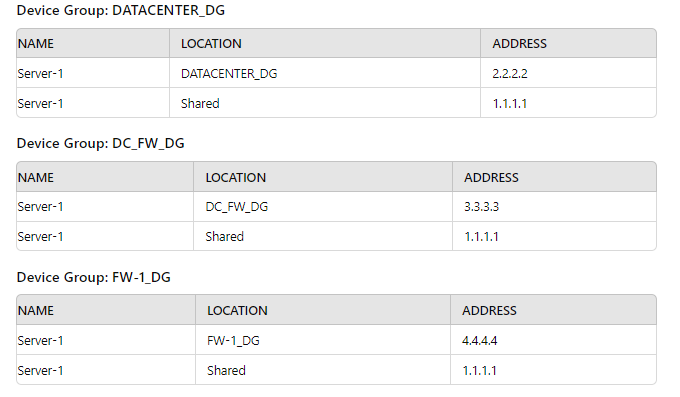
Review the screenshots and consider the following information:
1. FW-1is assigned to the FW-1_DG device group, and FW-2 is assigned to
OFFICE_FW_DC
2. There are no objects configured in REGIONAL_DG and OFFICE_FW_DG device groups.
Which IP address will be pushed to the firewalls inside Address Object Server-1?
A. Server-1 on FW-1 will have IP 4.4.4.4. Server-1 on FW-2 will have IP 1.1.1.1
B. Server-1 on FW-1 will have IR 111.1. Server-1 will not be pushed to FW-2.
C. Server-1 on FW-1 will have IP 2.2.2.2. Server-1 will not be pushed to FW-2.
D. Server-1 on FW-1 will have IP 3.3.3.3. Server-1 will not be pushed to FW-2.
Explanation: Device Group Hierarchy
Shared
DATACENTER_DG
DC_FW_DG
REGIONAL_DG
OFFICE_FW_DG
FW-1_DG
Analysis
Considerations:
FW-1 is assigned to the FW-1_DG device group.
FW-2 is assigned to the OFFICE_FW_DG device group.
There are no objects configured in REGIONAL_DG and OFFICE_FW_DG device
groups.
The address object Server-1 appears in multiple device groups with different IP addresses.
The device groups have a hierarchy, which means objects can be inherited from parent
groups unless overridden in the child group.
To ensure that a Security policy has the highest priority, how should an administrator configure a Security policy in the device group hierarchy?
A. Add the policy to the target device group and apply a master device to the device group.
B. Reference the targeted device's templates in the target device group.
C. Clone the security policy and add it to the other device groups.
D. Add the policy in the shared device group as a pre-rule
A standalone firewall with local objects and policies needs to be migrated into Panorama. What procedure should you use so Panorama is fully managing the firewall?
A. Use the "import device configuration to Panorama" operation, commit to Panorama, then "export or push device config bundle" to push the configuration.
B. Use the "import Panorama configuration snapshot" operation, commit to Panorama, then "export or push device config bundle" to push the configuration.
C. Use the "import device configuration to Panorama" operation, commit to Panorama, then perform a device-group commit push with "include device and network templates".
D. Use the "import Panorama configuration snapshot" operation, commit to Panorama, then perform a device-group commit push with "include device and network templates".
An administrator is informed that the engineer who previously managed all the VPNs has left the company. According to company policies the administrator must update all the IPSec VPNs with new pre-shared keys Where are the pre-shared keys located on the firewall?
A. Network/lPSec Tunnels
B. Network/Network Profiles/IKE Gateways
C. Network/Network ProfilesTlPSec Crypto
D. Network/Network Profiles/IKE Crypto
A new application server 192.168.197.40 has been deployed in the DMZ. There are no public IP addresses available resulting in the server sharing MAT IP 198 51 100 B8 with another OMZ serve that uses IP address 192 168 19? 60 Firewall security and NAT rules have been configured The application team has confirmed mat the new server is able to establish a secure connection to an external database with IP address 203.0.113.40. The database team reports that they are unable to establish a secure connection to 196 51 100 88 from 203.0.113.40 However it confirm a successful prig test to 198 51 100 88 Referring to the MAT configuration and traffic logs provided how can the firewall engineer resolve the situation and ensure inbound and outbound connections work concurrently for both DMZ servers?
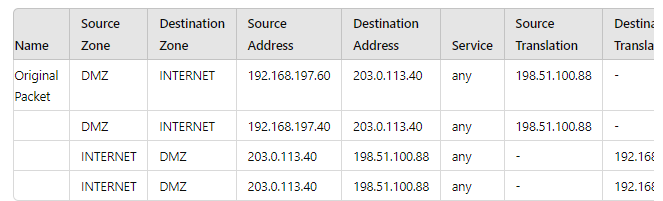
A. Replace the two NAT rules with a single rule that has both DMZ servers as "Source Address." both external servers as "Destination Address." and Source Translation remaining as is with bidirectional option enabled
B. Sharing a single NAT IP is possible for outbound connectivity not for inbound, therefore, a new public IP address must be obtained for the new DMZ server and used in the NAT rule 6 DMZ server 2.
C. Configure separate source NAT and destination NAT rules for the two DMZ servers without using the bidirectional option.
D. Move the NAT rule 6 DMZ server 2 above NAT rule 5 DMZ server 1.
Explanation: The table displays NAT rules configured on the firewall. The key points are:
The firewall team has been asked to deploy a new Panorama server and to forward all firewall logs to this server By default, which component of the Palo Alto Networks firewall architect is responsible for log forwarding and should be checked for early signs of overutilization?
A. Management plane CPU
B. Dataplane CPU
C. Packet buffers
D. On-chip packet descriptors
A company has configured GlobalProtect to allow their users to work from home. A decrease in performance for remote workers has been reported during peak-use hours. Which two steps are likely to mitigate the issue? (Choose TWO)
A. Exclude video traffic
B. Enable decryption
C. Block traffic that is not work-related
D. Create a Tunnel Inspection policy
An administrator is configuring a Panorama device group. Which two objects are configurable? (Choose two.)
A. DNS Proxy
B. SSL/TLS profiles
C. address groups
D. URL Filtering profiles
An engineer is configuring a Protection profile to defend specific endpoints and resources
against malicious activity.
The profile is configured to provide granular defense against targeted flood attacks for
specific critical systems that are accessed by users from the internet.
Which profile is the engineer configuring?
A. Packet Buffer Protection
B. Zone Protection
C. Vulnerability Protection
D. DoS Protection
Explanation: The engineer is configuring a DoS Protection profile to defend specific endpoints and resources against malicious activity. A DoS Protection profile is a feature that enables the firewall to detect and prevent denial-of-service (DoS) attacks that attempt to overwhelm network resources or disrupt services. A DoS Protection profile can provide granular defense against targeted flood attacks for specific critical systems that are accessed by users from the internet, such as web servers, DNS servers, or VPN gateways. A DoS Protection profile can be applied to a security policy rule that matches the traffic to and from the protected systems, and can specify the thresholds and actions for different types of flood attacks, such as SYN, UDP, ICMP, or other IP floods12. References: DoS Protection, PCNSE Study Guide (page 58)
| Page 7 out of 27 Pages |
| Previous |