A network administrator wants to deploy SSL Forward Proxy decryption. What two attributes should a forward trust certificate have? (Choose two.)
A. A subject alternative name
B. A private key
C. A server certificate
D. A certificate authority (CA) certificate
Explanation: The two attributes that a forward trust certificate should have for SSL
Forward Proxy decryption are:
B: A private key: This is the key that the firewall uses to sign the certificates that it
generates for the decrypted sessions. The private key must be securely stored on
the firewall and not shared with anyone1.
D: A certificate authority (CA) certificate: This is the certificate that the firewall uses
to issue the certificates for the decrypted sessions. The CA certificate must be
trusted by the client browsers and devices that receive the certificates from the
firewall1.
An engineer needs to permit XML API access to a firewall for automation on a network segment that is routed through a Layer 3 sub-interface on a Palo Alto Networks firewall. However, this network segment cannot access the dedicated management interface due to the Security policy. Without changing the existing access to the management interface, how can the engineer fulfill this request?
A. Specify the subinterface as a management interface in Setup > Device > Interfaces.
B. Add the network segment's IP range to the Permitted IP Addresses list.
C. Enable HTTPS in an Interface Management profile on the subinterface
D. Configure a service route for HTTP to use the subinterface.
Explanation: To enable XML API access to a firewall for automation from a network
segment routed through a Layer 3 sub-interface, the most straightforward approach is to
use an Interface Management profile.
C. This can be achieved by:
Configuring an Interface Management profile and enabling HTTPS access on it.
This profile defines management services that are permitted on the interface,
including HTTPS, which is required for XML API access.
Applying this Interface Management profile to the desired Layer 3 sub-interface.
This action enables HTTPS access (and thus XML API access) on the subinterface,
allowing devices on the connected network segment to communicate
with the firewall for automation purposes.
This solution allows for the secure extension of management capabilities to network
segments without direct access to the dedicated management interface, facilitating
automation and operational efficiency without necessitating changes to existing access
configurations.
A company is deploying User-ID in their network. The firewall team needs to have the ability to see and choose from a list of usernames and user groups directly inside the Panorama policies when creating new security rules. How can this be achieved?
A. By configuring Data Redistribution Client in Panorama > Data Redistribution
B. By configuring User-ID group mapping in Panorama > User Identification
C. By configuring User-ID source device in Panorama > Managed Devices
D. By configuring Master Device in Panorama > Device Groups
Explanation: To enable the firewall team to view and select from a list of usernames and user groups directly within Panorama policies for new security rule creation, User-ID group mapping should be configured in Panorama under User Identification. This feature allows Panorama to collect user and group information from various sources (like Active Directory) and use this information to create policies. By setting up User-ID group mapping, administrators can leverage user identity as criteria in security rules, enabling more granular access control and policy enforcement based on user or group membership, thereby enhancing the overall security posture.
Which type of policy in Palo Alto Networks firewalls can use Device-ID as a match condition?
A. NAT
B. DOS protection
C. QoS
D. Tunnel inspection
Explanation: The type of policy in Palo Alto Networks firewalls that can use Device-ID as a match condition is QoS. This is because Device-ID is a feature that allows the firewall to identify and classify devices on the network based on their characteristics, such as vendor, model, OS, and role1. QoS policies are used to allocate bandwidth and prioritize traffic based on various criteria, such as application, user, source, destination, and device2. By using Device-ID as a match condition in QoS policies, the firewall can apply different QoS actions to different types of devices, such as IoT devices, laptops, smartphones, etc3. This can help optimize the network performance and ensure the quality of service for critical applications and devices.
Exhibit.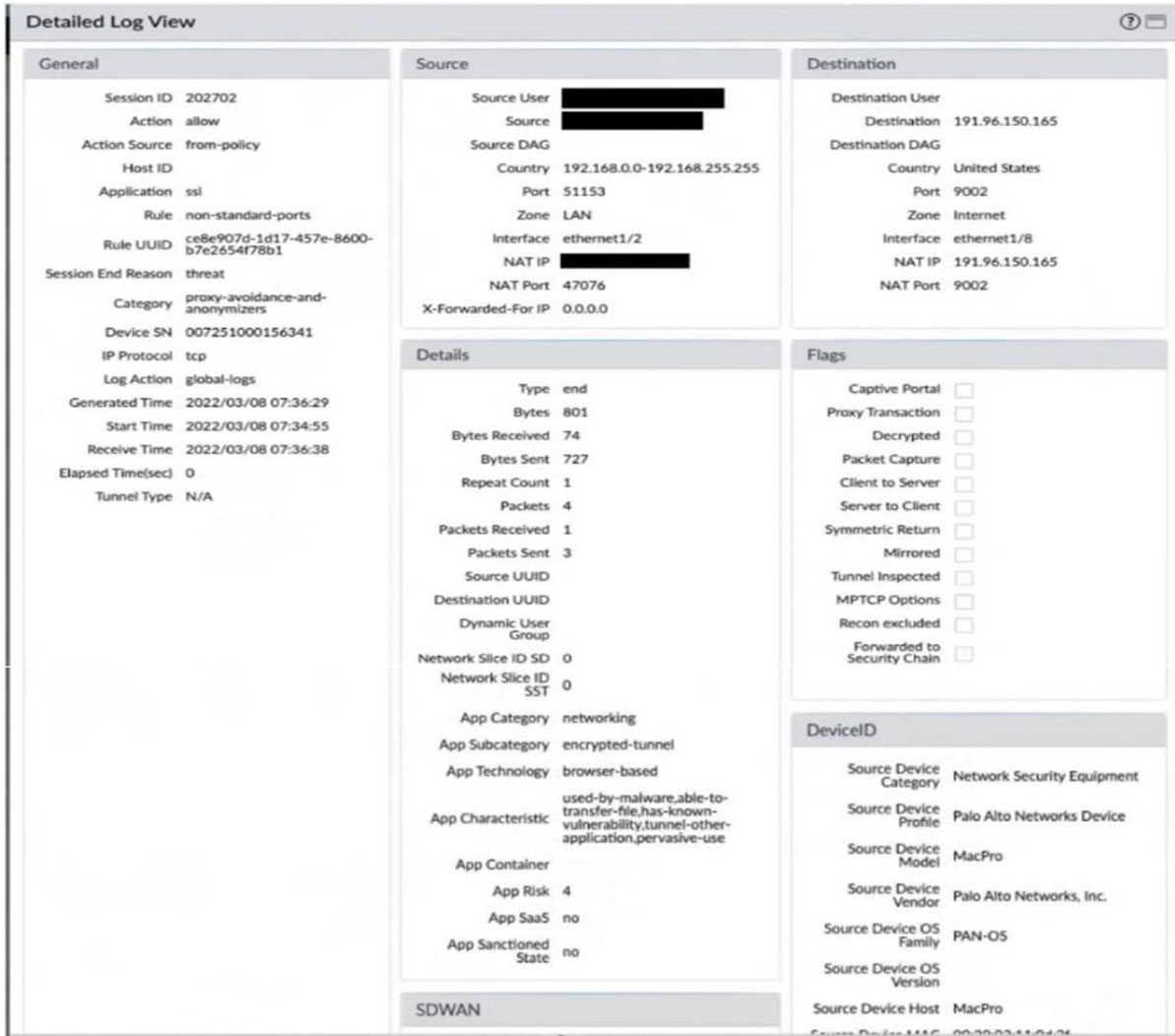
Given the screenshot, how did the firewall handle the traffic?
A. Traffic was allowed by profile but denied by policy as a threat.
B. Traffic was allowed by policy but denied by profile as a threat.
C. Traffic was allowed by policy but denied by profile as encrypted.
D. Traffic was allowed by policy but denied by profile as a nonstandard port.
An administrator needs to validate that policies that will be deployed will match the appropriate rules in the device-group hierarchy. Which tool can the administrator use to review the policy creation logic and verify that unwanted traffic is not allowed?
A. Preview Changes
B. Managed Devices Health
C. Test Policy Match
D. Policy Optimizer
Explanation: The Test Policy Match tool in Palo Alto Networks' management systems
(such as Panorama or the firewall interface) allows administrators to simulate traffic against
configured security policies. This tool is critical for ensuring that the correct policies are
applied to specific traffic patterns and that no unintended access is granted.
Test Policy Match enables you to input parameters like source IP, destination IP,
application, user, and more, and the system will determine which policy would
apply.
It is especially useful for verifying the device-group hierarchy in multi-tenant or
Panorama-managed environments, ensuring that inherited or overridden rules are
correctly applied.
The tool also helps to proactively check that traffic will be blocked or allowed as
intended, reducing misconfigurations and preventing unwanted traffic.
A. Preview Changes: This feature is used to review configuration changes before
committing them but does not simulate or validate policy matches.
B. Managed Devices Health: This option is related to checking the health and
connectivity status of managed devices, not policies.
D. Policy Optimizer: This tool is used to refine existing security policies by
identifying overly permissive rules or unused objects, not for testing specific traffic
matches.
Key Points: Why not the other options? The Test Policy Match tool is the most appropriate
choice for the scenario described.
An administrator notices interface ethernet1/2 failed on the active firewall in an active / passive firewall high availability (HA) pair Based on the image below what - if any - action was taken by the active firewall when the link failed?
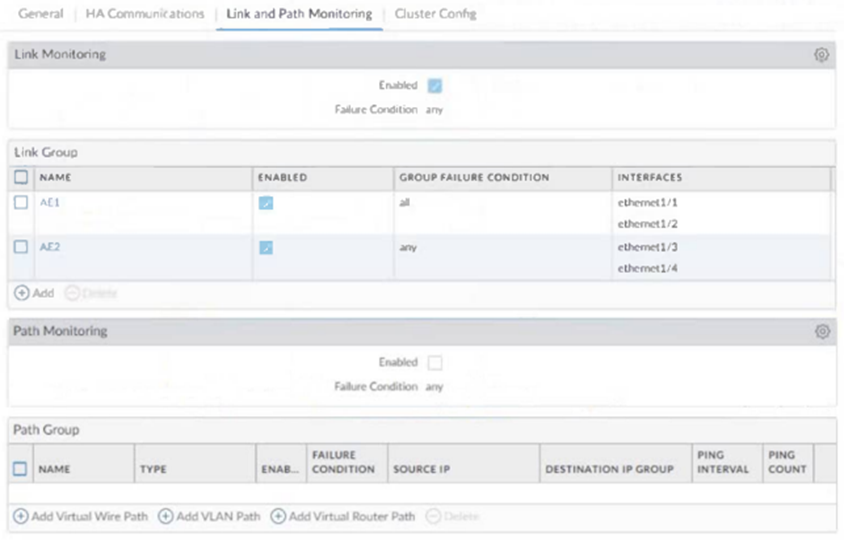
A. The active firewall failed over to the passive HA member because "any" is selected for the Link Monitoring
B. No action was taken because Path Monitoring is disabled
C. No action was taken because interface ethernet1/1 did not fail
D. The active firewall failed over to the passive HA member due to an AE1 Link Group failure
What must be configured to apply tags automatically based on User-ID logs?
A. Device ID
B. Log Forwarding profile
C. Group mapping
D. Log settings
Explanation:
To apply tags automatically based on User-ID logs, the engineer must
configure a Log Forwarding profile that specifies the criteria for matching the logs and the
tags to apply. The Log Forwarding profile can be attached to a security policy rule or a
decryption policy rule to enable auto-tagging for the traffic that matches the rule. The tags
can then be used for dynamic address groups, policy enforcement, or
reporting1.
References:
Use Auto-Tagging to Automate Security Actions, PCNSE Study Guide (page 49)
An administrator is using Panorama to manage multiple firewalls. After upgrading all
devices to the latest PAN-OS software, the administrator enables log forwarding from the
firewalls to Panorama.
However, pre-existing logs from the firewalls are not appearing in Panorama.
Which action should be taken to enable the firewalls to send their pre-existing logs to
Panorama?
A. Export the log database.
B. Use the import option to pull logs.
C. Use the scp logdb export command.
D. Use the ACC to consolidate the logs.
A firewall engineer is tasked with defining signatures for a custom application. Which two sources can the engineer use to gather information about the application patterns'? (Choose two.)
A. Traffic logs
B. Data filtering logs
C. Policy Optimizer
D. Wireshark
Explanation: To determine which sources an engineer can use to gather information about
application patterns for creating custom signatures, let’s analyze each option based on
PAN-OS 11.0 documentation and typical network troubleshooting practices.
A. Traffic Logs
Why It’s Correct:
How to Use:
Documentation Reference:
B. Data Filtering Logs
Why It’s Incorrect:
Documentation Reference:
C. Policy Optimizer
Why It’s Incorrect:
Documentation Reference:
D. Wireshark
Why It’s Correct:
How to Use:
Documentation Reference:
Summary of Correct Choices
Traffic Logs:
Wireshark:
Which two scripting file types require direct upload to the Advanced WildFire portal/API for analysis? (Choose two.)
A. Ps1
B. Perl
C. Python
D. VBS
An engineer has been asked to limit which routes are shared by running two different areas within an OSPF implementation. However, the devices share a common link for communication. Which virtual router configuration supports running multiple instances of the OSPF protocol over a single link?
A. OSPFV3
B. ECMP
C. ASBR
D. OSBF
| Page 5 out of 27 Pages |
| Previous |