You are running a diagnose command continuously as traffic flows through a platform with
NP6 and you obtain the following output:
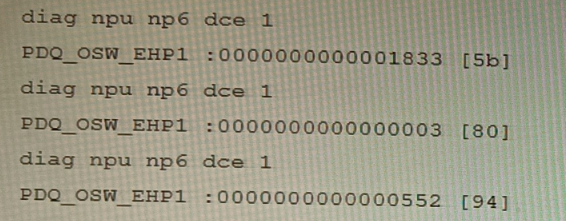
Given the information shown in the output, which two statements are true? (Choose two.)
A. Enabling bandwidth control between the ISF and the NP will change the output
B. The output is showing a packet descriptor queue accumulated counter
C. Enable HPE shaper for the NP6 will change the output
D. Host-shortcut mode is enabled.
E. There are packet drops at the XAUI.
Explanation: The diagnose command shown in the output is used to display information
about NP6 packet descriptor queues. The output shows that there are 16 NP6 units in total,
and each unit has four XAUI ports (XA0-XA3). The output also shows that there are some
non-zero values in the columns PDQ ACCU (packet descriptor queue accumulated
counter) and PDQ DROP (packet descriptor queue drop counter). These values indicate
that there are some packet descriptor queues that have reached their maximum capacity
and have dropped some packets at the XAUI ports. This could be caused by congestion or
misconfiguration of the XAUI ports or the ISF (Internal Switch Fabric).
The output is showing a packet descriptor queue accumulated counter, which is a measure
of the number of packets that have been dropped by the NP6 due to congestion. The
counter will increase if there are more packets than the NP6 can handle, which can happen
if the bandwidth between the ISF and the NP is not sufficient or if the HPE shaper is
enabled.
The output also shows that there are packet drops at the XAUI, which is the interface
between the NP6 and the FortiGate's backplane. This means that the NP6 is not able to
keep up with the traffic and is dropping packets.
The other statements are not true. Host-shortcut mode is not enabled, and enabling
bandwidth control between the ISF and the NP will not change the output. HPE shaper is a
feature that can be enabled to improve performance, but it will not change the output of the
diagnose command.
You are responsible for recommending an adapter type for NICs on a FortiGate VM that will run on an ESXi Hypervisor. Your recommendation must consider performance as the main concern, cost is not a factor. Which adapter type for the NICs will you recommend?
A. Native ESXi Networking with E1000
B. Virtual Function (VF) PCI Passthrough
C. Native ESXi Networking with VMXNET3
D. Physical Function (PF) PCI Passthrough
Explanation: The FortiGate VM is a virtual firewall appliance that can run on various hypervisors, such as ESXi, Hyper-V, KVM, etc. The adapter type for NICs on a FortiGate VM determines the performance and compatibility of the network interface cards with the hypervisor and the physical network. There are different adapter types available for NICs on a FortiGate VM, such as E1000, VMXNET3, SR-IOV, etc. If performance is the main concern and cost is not a factor, one option is to use native ESXi networking with VMXNET3 adapter type for NICs on a FortiGate VM that will run on an ESXi hypervisor. VMXNET3 is a paravirtualized network interface card that is optimized for performance in virtual machines and supports features such as multiqueue support, Receive Side Scaling (RSS), Large Receive Offload (LRO), IPv6 offloads, and MSI/MSI-X interrupt delivery. Native ESXi networking means that the FortiGate VM uses the standard virtual switch (vSwitch) or distributed virtual switch (dvSwitch) provided by the ESXi hypervisor to connect to the physical network. This option can provide high performance and compatibility for NICs on a FortiGate VM without requiring additional hardware or software components.
Refer to the CLI output:
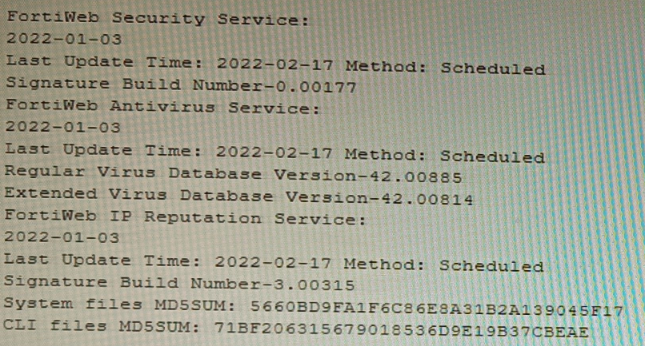
Given the information shown in the output, which two statements are correct? (Choose
two.)
A. Geographical IP policies are enabled and evaluated after local techniques.
B. Attackers can be blocked before they target the servers behind the FortiWeb.
C. The IP Reputation feature has been manually updated
D. An IP address that was previously used by an attacker will always be blocked
E. Reputation from blacklisted IP addresses from DHCP or PPPoE pools can be restored
Explanation: The CLI output shown in the exhibit indicates that FortiWeb has enabled IP
Reputation feature with local techniques enabled and geographical IP policies enabled
after local techniques (set geoip-policy-order after-local). IP Reputation feature is a feature
that allows FortiWeb to block or allow traffic based on the reputation score of IP addresses,
which reflects their past malicious activities or behaviors. Local techniques are methods
that FortiWeb uses to dynamically update its own blacklist based on its own detection of
attacks or violations from IP addresses (such as signature matches, rate limiting, etc.).
Geographical IP policies are rules that FortiWeb uses to block or allow traffic based on the
geographical location of IP addresses (such as country, region, city, etc.). Therefore, based
on the output, one correct statement is that attackers can be blocked before they target the
servers behind the FortiWeb. This is because FortiWeb can use IP Reputation feature to
block traffic from IP addresses that have a low reputation score or belongto a blacklisted
location, which prevents them from reaching the servers and launching attacks. Another correct statement is that reputation from blacklisted IP addresses from DHCP or PPPoE
pools can be restored. This is because FortiWeb can use local techniques to remove IP
addresses from its own blacklist if they stop sending malicious traffic for a certain period of
time (set local-techniques-expire-time), which allows them to regain their reputation and
access the servers. This is useful for IP addresses that are dynamically assigned by DHCP
or PPPoE and may change frequently.
Refer to the exhibit, which shows the high availability configuration for the
FortiAuthenticator (FAC1).
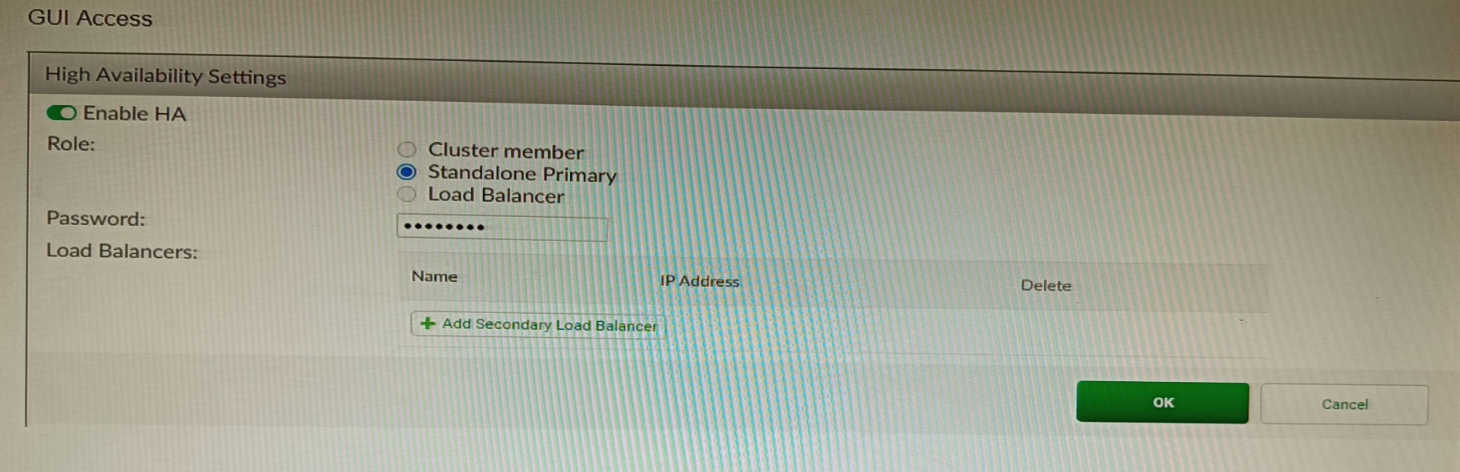
Based on this information, which statement is true about the next FortiAuthenticator (FAC2)
member that will join an HA cluster with this FortiAuthenticator (FAC1)?
A. FAC2 can only process requests when FAC1 fails.
B. FAC2 can have its HA interface on a different network than FAC1.
C. The FortiToken license will need to be installed on the FAC2.
D. FSSO sessions from FAC1 will be synchronized to FAC2.
Explanation: When FortiAuthenticator operates in cluster mode, it provides active-passive failover and synchronization of all configuration and data, including FSSO sessions, between the cluster members. Therefore, if FAC1 is the active unit and FAC2 is the standby unit, any FSSO sessions from FAC1 will be synchronized to FAC2. If FAC1 fails, FAC2 will take over the active role and continue to process the FSSO sessions.
Which two methods are supported for importing user defined Lookup Table Data into the FortiSIEM? (Choose two.)
A. Report
B. FTP
C. API
D. SCP
Explanation: FortiSIEM supports two methods for importing user defined Lookup Table
Data:
Report: You can import lookup table data from a report. This is the most common
method for importing lookup table data.
API: You can also import lookup table data using the FortiSIEM API. This is a
more advanced method that allows you to import lookup table data
programmatically.
FTP, SCP, and other file transfer protocols are not supported for importing lookup table
data into FortiSIEM.
An HA topology is using the following configuration:
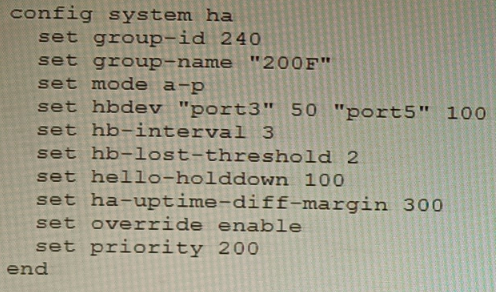
Based on this configuration, how long will it take for a failover to be detected by the
secondary cluster member?
A. 600ms
B. 200ms
C. 300ms
D. 100ms
Explanation: The HA heartbeat interval is 100ms, and the number of lost heartbeats before a failover is detected is 2. So, it will take 2 * 100ms = 200ms for a failover to be detected by the secondary cluster member.
Refer to the exhibits, which show a firewall policy configuration and a network topology.
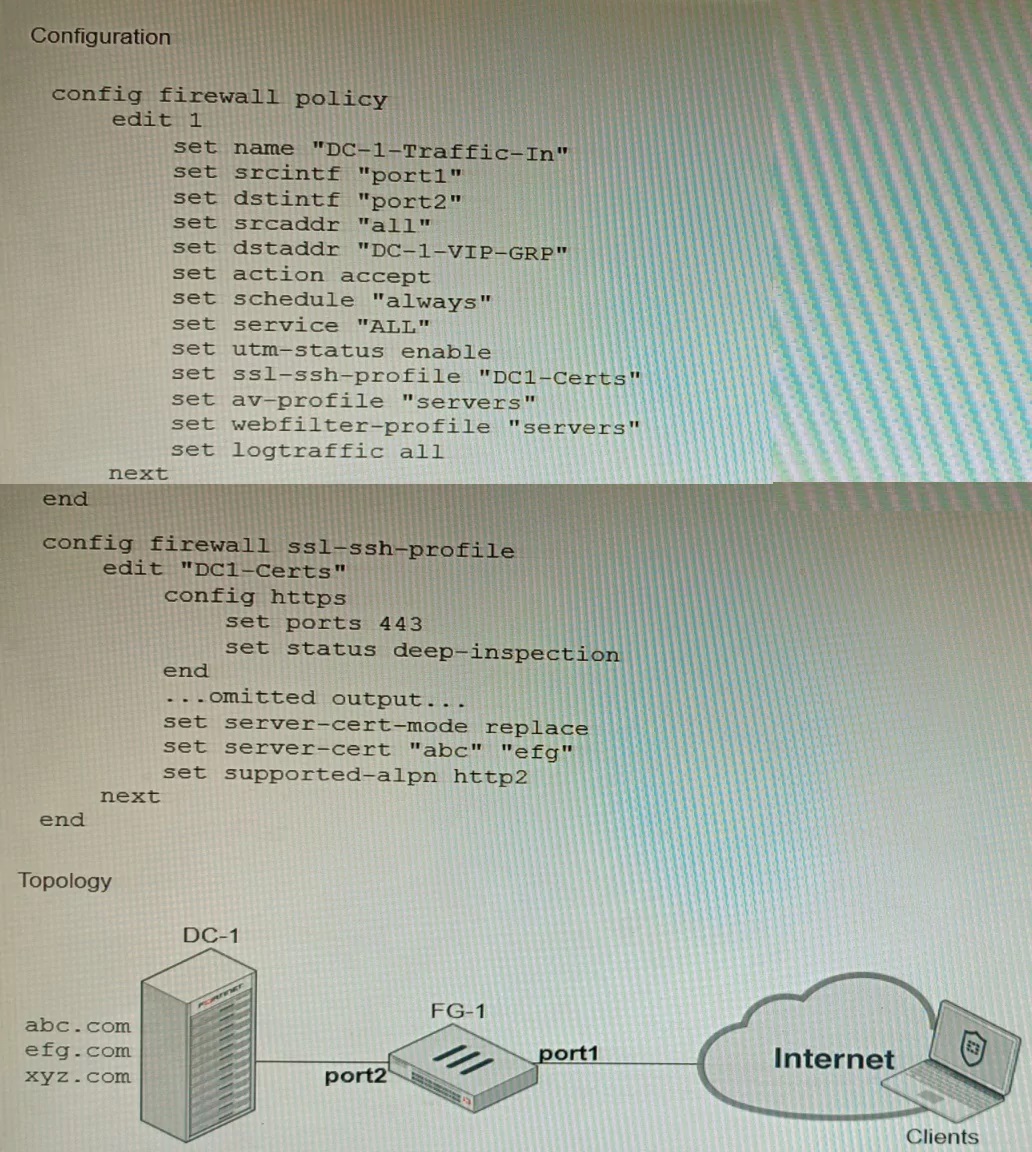
An administrator has configured an inbound SSL inspection profile on a FortiGate device
(FG-1) that is protecting a data center hosting multiple web pages-Given the scenario
shown in the exhibits, which certificate will FortiGate use to handle requests to xyz.com?
A. FortiGate will fall-back to the default Fortinet_CA_SSL certificate.
B. FortiGate will reject the connection since no certificate is defined.
C. FortiGate will use the Fortinet_CA_Untrusted certificate for the untrusted connection,
D. FortiGate will use the first certificate in the server-cert list—the abc.com certificate
Explanation: When using inbound SSL inspection, FortiGate needs to present a certificate to the client that matches the requested domain name. If no matching certificate is found in the server-cert list, FortiGate will fall-back to the default Fortinet_CA_SSL certificate, which is self-signed and may trigger a warning on the client browser.
A. The FortiGate was not configured with the correct pre-shared key to connect to the FortiManager
B. The DHCP server was not configured with the FQDN of the FortiManager
C. The DHCP server used the incorrect option type for the FortiManager IP address.
D. The configuration was modified on the FortiGate prior to connecting to the FortiManager
Explanation: C is correct because the DHCP server used the incorrect option type for the FortiManager IP address. The option type should be 43 instead of 15, as shown in the FortiManager Administration Guide under Zero-Touch Provisioning > Configuring DHCP options for ZTP.
You are troubleshooting a FortiMail Cloud service integrated with Office 365 where outgoing emails are not reaching the recipients' mail What are two possible reasons for this problem? (Choose two.)
A. The FortiMail access control rule to relay from Office 365 servers FQDN is missing.
B. The FortiMail DKIM key was not set using the Auto Generation option.
C. The FortiMail access control rules to relay from Office 365 servers public IPs are missing.
D. A Mail Flow connector from the Exchange Admin Center has not been set properly to the FortiMail Cloud FQDN.
Explanation: A. The FortiMail access control rule to relay from Office 365 servers FQDN is
missing.
If the access control rule to relay from Office 365 servers FQDN is missing, then FortiMail
will not be able to send emails to Office 365. This is because the access control rule
specifies which IP addresses or domains are allowed to relay emails through FortiMail.
D. A Mail Flow connector from the Exchange Admin Center has not been set properly to
the FortiMail Cloud FQDN.
If the Mail Flow connector from the Exchange Admin Center is not set properly to the
FortiMail Cloud FQDN, then Office 365 will not be able to send emails to FortiMail. This is
because the Mail Flow connector specifies which SMTP server is used to send emails to
external recipients.
Refer to the exhibit.
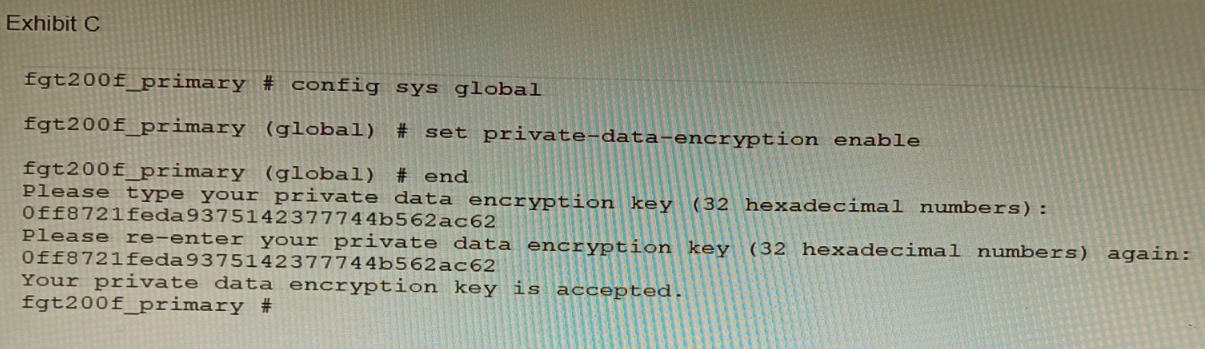
A customer has deployed a FortiGate 200F high-availability (HA) cluster that contains &
TPM chip. The exhibit shows output from the FortiGate CLI session where the
administrator enabled TPM.
Following these actions, the administrator immediately notices that both FortiGate high
availability (HA) status and FortiManager status for the FortiGate are negatively impacted.
What are the two reasons for this behavior? (Choose two.)
A. The private-data-encryption key entered on the primary did not match the value that the TPM expected.
B. Configuration for TPM is not synchronized between FortiGate HA cluster members.
C. The FortiGate has not finished the auto-update process to synchronize the new configuration to FortiManager yet.
D. TPM functionality is not yet compatible with FortiGate HA D The administrator needs to manually enter the hex private data encryption key in FortiManager
Explanation: The two reasons for the negative impact on the FortiGate HA status and
FortiManager status after enabling TPM are:
The private-data-encryption key entered on the primary unit did not match the
value that the TPM expected. This could happen if the TPM was previously
enabled and then disabled, and the key was changed in between. The TPM will
reject the new key and cause an error in the configuration synchronization.
Configuration for TPM is not synchronized between FortiGate HA cluster
members. Each cluster member must have the same private-data-encryption key
to form a valid HA cluster and synchronize their configurations. However, enabling
TPM on one unit does not automatically enable it on the other units, and the key
must be manually entered on each unit. To resolve these issues, the administrator
should disable TPM on all units, clear the TPM data, and then enable TPM again
with the same private-data-encryption key on each unit.
Refer to the exhibit.
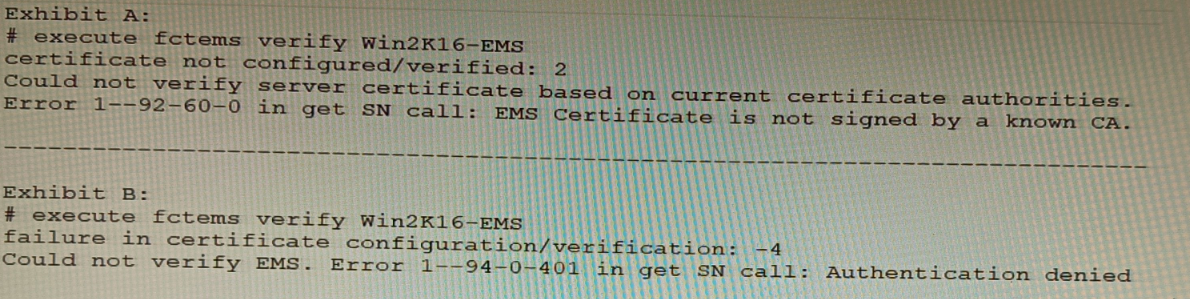
The exhibit shows two error messages from a FortiGate root Security Fabric device when
you try to configure a new connection to a FortiClient EMS Server.
Referring to the exhibit, which two actions will fix these errors? (Choose two.)
A. Verify that the CRL is accessible from the root FortiGate
B. Export and import the FortiClient EMS server certificate to the root FortiGate.
C. Install a new known CA on the Win2K16-EMS server.
D. Authorize the root FortiGate on the FortiClient EMS
Explanation:
A is correct because the error message "The CRL is not accessible" indicates that
the root FortiGate cannot access the CRL for the FortiClient EMS server. Verifying
that the CRL is accessible will fix this error.
D is correct because the error message "The FortiClient EMS server is not
authorized" indicates that the root FortiGate is not authorized to connect to the
FortiClient EMS server. Authorizing the root FortiGate on the FortiClient EMS
server will fix this error.
The other options are incorrect. Option B is incorrect because exporting and importing the
FortiClient EMS server certificate to the root FortiGate will not fix the CRL error. Option C is
incorrect because installing a new known CA on the Win2K16-EMS server will not fix the
authorization error.
Refer to the exhibits.
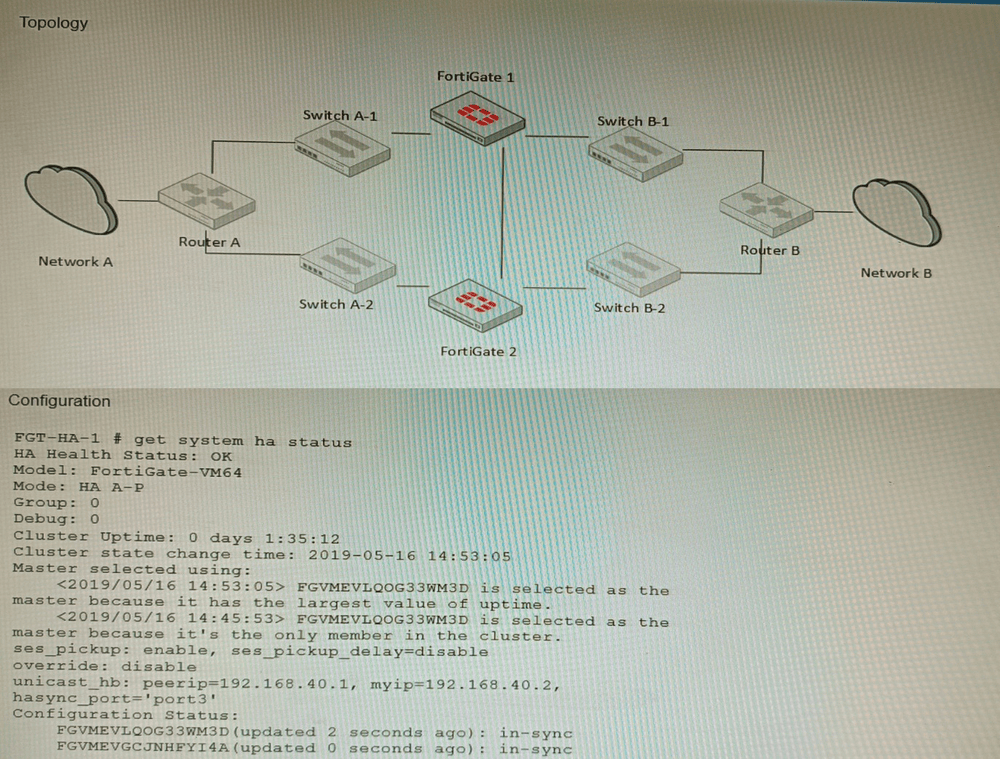
The exhibits show a FortiGate network topology and the output of the status of high
availability on the FortiGate.
Given this information, which statement is correct?
A. The ethertype values of the HA packets are 0x8890, 0x8891, and 0x8892
B. The cluster mode can support a maximum of four (4) FortiGate VMs
C. The cluster members are on the same network and the IP addresses were statically assigned.
D. FGVMEVLQOG33WM3D and FGVMEVGCJNHFYI4A share a virtual MAC address.
Explanation: The output of the status of high availability on the FortiGate shows that the cluster mode is active-passive, which means that only one FortiGate unit is active at a time, while the other unit is in standby mode. The active unit handles all traffic and also sends HA heartbeat packets to monitor the standby unit. The standby unit becomes active if it stops receiving heartbeat packets from the active unit, or if it receives a higher priority from another cluster unit. In active-passive mode, all cluster units share a virtual MAC address for each interface, which is used as the source MAC address for all packets forwarded by the cluster.
| Page 1 out of 5 Pages |