As part of your analysis, you discover that an incident is a false positive.
You change the incident status to Closed: False Positive.
Which statement about your update is true?
A. The audit history log will be updated.
B. The corresponding event will be marked as mitigated.
C. The incident will be deleted.
D. The incident number will be changed
Explanation: When an incident in FortiAnalyzer is identified as a false positive and its
status is updated to "Closed: False Positive," certain records and logs are updated to
reflect this change.
Option A - The Audit History Log Will Be Updated:
Option B - The Corresponding Event Will Be Marked as Mitigated:
Option C - The Incident Will Be Deleted:
Option D - The Incident Number Will Be Changed:
Conclusion:
Correct Answer: A. The audit history log will be updated.
This is the most accurate answer, as the update to "Closed: False Positive" is
recorded in FortiAnalyzer’s audit history log for accountability and tracking
purposes.
References:
FortiAnalyzer 7.4.1 documentation on incident management and audit history
logging.
After a generated a repot, you notice the information you were expecting to see in not
included in it. However, you confirm that the logs are there:
Which two actions should you perform? (Choose two.)
A. Check the time frame covered by the report.
B. Disable auto-cache.
C. Increase the report utilization quota.
D. Test the dataset.
What is the purpose of running the command diagnose sql status sqlreportd?
A. To view a list of scheduled reports
B. To list the current SQL processes running
C. To display the SQL query connections and hcache status
D. To identify the database log insertion status
Explanation: The command diagnose sql status sqlreportd is used in FortiAnalyzer to
obtain specific information about the SQL reporting process and caching status. Here’s
what this command accomplishes and an analysis of each option:
Command Functionality:
Option Analysis:
Conclusion:
Correct Answer: C. To display the SQL query connections and hcache status
This command is used to monitor SQL reporting activities and cache status, aiding
in the analysis of report generation performance and connection health.
Which SQL query is in the correct order to query to database in the FortiAnalyzer?
A. SELECT devid FROM $log GROUP BY devid WHERE ‘user’,,’ users1’
B. SELECT FROM $log WHERE devid ‘user’,, USER1’ GROUP BY devid
C. SELCT devid WHERE ’user’-‘ USER1’ FROM $log GROUP By devid
D. SELECT devid FROM $log WHERE ‘user’=’ GROUP BY devid
Explanation: In FortiAnalyzer’s SQL query syntax, the typical order for querying the
database follows the standard SQL format, which is:
Why must you wait for several minutes before you run a playbook that you just created? A. FortiAnalyzer needs that time to parse the new playbook. B. FortiAnalyzer needs that time to debug the new playbook. C. FortiAnalyzer needs that time to back up the current playbooks. D. FortiAnalyzer needs that time to ensure there are no other playbooks running
Explanation: When a new playbook is created on FortiAnalyzer, the system requires some
time to parse and validate the playbook before it can be executed. Parsing involves
checking the playbook's structure, ensuring that all syntax and logic are correct, and
preparing the playbook for execution within FortiAnalyzer’s automation engine. This initial
parsing step is necessary for FortiAnalyzer to load the playbook into its operational
environment correctly.
Which FortiAnalyzer feature allows you to use a proactive approach when managing your
network security? A. FortiView Monitor B. Outbreak alert services C. Incidents dashboard D. Threat hunting
Explanation: FortiAnalyzer offers several features for monitoring, alerting, and incident
management, each serving different purposes. Let's examine each option to determine
which one best supports a proactive security approach.
Exhibit. A. Operation-login and performed_on==’’GUI(10.1.1.100)’ and user!=admin B. Operation-login and performed_on==’’GU (10.1.1.120)’ and user!=admin C. Operation-login and srcip== 10.1.1.100 and dstip==10.1.1.1.210 and user==admin D. Operation-login and dstip==10.1.1.210 and user!-admin
Explanation: The objective is to create a filter that identifies all login attempts to the
FortiAnalyzer web interface (GUI) coming from Laptop1 (IP 10.1.1.100) and excludes the
admin user. This filter should match any user other than admin.
Which statement describes archive logs on FortiAnalyzer? A. Logs that are indexed and stored in the SQL database B. Logs a FortiAnalyzer administrator can access in FortiView C. Logs compressed and saved in files with the .gz extension D. Logs previously collected from devices that are offline
Explanation: In FortiAnalyzer, archive logs refer to logs that have been compressed and
stored to save space. This process involves compressing the raw log files into the .gz
format, which is a common compression format used in Fortinet systems for archived data.
Exhibit. A. They can be downloaded to a file. B. They are sortable by columns and customizable. C. They are not available for analysis in FortiView. D. They were searched by using text mode.
Explanation: In this exhibit, we observe a search query on the FortiAnalyzer interface
displaying log data with details about the connection events, including fields like date, srcip,
dstip, service, and dstintf. This setup allows for several functionalities within FortiAnalyzer.
Which statement about sending notifications with incident update is true? A. You can send notifications to multiple external platforms. B. Notifications can be sent only by email. C. If you use multiple fabric connectors, all connectors must have the same settings. D. Notifications can be sent only when an incident is updated or deleted.
Explanation: In FortiOS and FortiAnalyzer, incident notifications can be sent to multiple
external platforms, not limited to a single method such as email. Fortinet's security fabric
and integration capabilities allow notifications to be sent through various fabric connectors
and third-party integrations. This flexibility is designed to ensure that incident updates
reach relevant personnel or systems using preferred communication channels, such as
email, Syslog, SNMP, or integration with SIEM platforms.
What happens when the indicator of compromise (IOC) engine on FortiAnalyzer finds web
logs that match blacklisted IP addresses? A. FortiAnalyzer flags the associated host for further analysis. B. A new infected entry is added for the corresponding endpoint under Compromised
Hosts. C. The detection engine classifies those logs as Suspicious. D. The endpoint is marked as Compromised and, optionally, can be put in quarantine.
A playbook contains five tasks in total. An administrator runs the playbook and four out of
five tasks finish successfully, but one task fails. A. Attention required B. Upstream_failed C. Failed D. Success
Explanation:
In FortiAnalyzer, when a playbook is run, each task’s status impacts the overall playbook
status. Here’s what happens based on task outcomes:
SELECT WHERE
Let’s briefly examine why the other options are incorrect:
Option A: SELECT devid FROM $log GROUP BY devid WHERE 'user', 'users1'
Option B: SELECT FROM $log WHERE devid 'user', USER1' GROUP BY devid
Option C: SELCT devid WHERE 'user' - 'USER1' FROM $log GROUP BY devid
References: FortiAnalyzer documentation for SQL queries indicates that the standard SQL
order should be followed when querying logs in FortiAnalyzer. Queries should follow the
format SELECT ... FROM ... WHERE ... GROUP BY ..., as demonstrated in option D.
A. FortiAnalyzer needs that time to parse the new playbook.
Here’s why the other options are incorrect:
Option A: FortiAnalyzer needs that time to parse the new playbook
Option B: FortiAnalyzer needs that time to debug the new playbook
Option C: FortiAnalyzer needs that time to back up the current playbooks
Option D: FortiAnalyzer needs that time to ensure there are no other playbooks
running
References: FortiAnalyzer documentation states that after creating a playbook, a brief
delay is expected as the system parses and validates the playbook. This ensures that any
syntax errors or logical inconsistencies are resolved before the playbook is executed,
making option A the correct answer.
D. Threat hunting
Option A - FortiView Monitor:
Option B - Outbreak Alert Services:
Option C - Incidents Dashboard:
Option D - Threat Hunting:
Conclusion:
Correct Answer: D. Threat hunting
Threat hunting is the most proactive feature among the options, as it involves
actively searching for threats within the network rather than reacting to already
detected incidents.
References:
FortiAnalyzer 7.4.1 documentation on Threat Hunting and proactive security
measures.
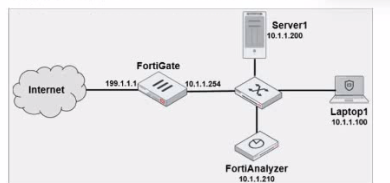
Laptop1 is used by several administrators to manage FotiAnalyzer. You want to configure a
generic text filter that matches all login attempts to the web interface generated by any user
other than admin’’, and coming from Laptop1.
Which filter will achieve the desired result?
A. Operation-login and performed_on==’’GUI(10.1.1.100)’ and user!=admin
Filter Components Analysis:
Option Analysis:
Conclusion:
Correct Answer: A. Operation-login and performed_on==’’GUI(10.1.1.100)’ and
user!=admin
This filter precisely captures the required conditions: login attempts from Laptop1
to the GUI interface by any user except admin.
References:
FortiAnalyzer 7.4.1 documentation on log filters, syntax for login operations, and
GUI login tracking.
C. Logs compressed and saved in files with the .gz extension
Archiving is essential in FortiAnalyzer to optimize storage and manage long-term retention
of logs without impacting performance.
Let’s examine each option for clarity:
Option A: Logs that are indexed and stored in the SQL database
Option B: Logs a FortiAnalyzer administrator can access in FortiView
Option C: Logs compressed and saved in files with the .gz extension
Option D: Logs previously collected from devices that are offline
References: FortiAnalyzer 7.4.1 documentation and configuration guides outline that
archived logs are stored in compressed files with the .gz extension to conserve storage
space, ensuring FortiAnalyzer can handle a larger volume of logs over extended periods.
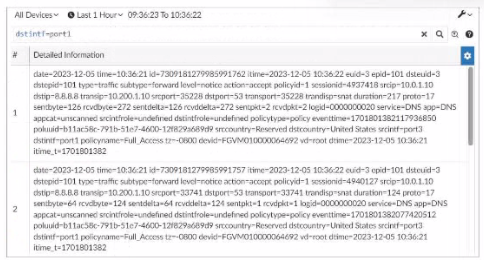
What can you conclude about these search results? (Choose two.)
A. They can be downloaded to a file.
D. They were searched by using text mode.
Option A - Download Capability:
Option B - Sorting and Customization:
Option C - Availability in FortiView:
Option D - Text Mode Search:
Conclusion:
Correct Answer: A. They can be downloaded to a file. and B. They are sortable by
columns and customizable.
These options are consistent with FortiAnalyzer's capabilities for managing,
exporting, and customizing log data.
References:
FortiAnalyzer 7.4.1 documentation on search, export functionalities, and
customizable views.
A. You can send notifications to multiple external platforms.
Let’s review each answer option for clarity:
Option A: You can send notifications to multiple external platforms
Option B: Notifications can be sent only by email
Option C: If you use multiple fabric connectors, all connectors must have the same
settings
Option D: Notifications can be sent only when an incident is updated or deleted
References: According to FortiOS and FortiAnalyzer 7.4.1 documentation, notifications for
incidents can be configured across various platforms by using multiple connectors, and
they are not limited to email alone. This capability is part of the Fortinet Security Fabric,
allowing for a broad range of integrations with external systems and platforms for effective
incident response.
B. A new infected entry is added for the corresponding endpoint under Compromised
Hosts.
What will be the status of the playbook after it is run?
A. Attention required
Status When All Tasks Succeed:
Status When Some Tasks Fail:
Option Analysis:
Conclusion:
Correct Answer: A. Attention required
The playbook status reflects that it completed, but an error occurred in one of the
tasks, prompting the administrator to review the failed task.
References:
FortiAnalyzer 7.4.1 documentation on playbook execution statuses and task error
handling.
Page 1 out of 5 Pages