Topic 1: Exam Pool A
Suppose your company has just passed a security risk assessment exercise. The results
display that the risk of the breach in the main company application is 50%. Security staff
has taken some measures and
implemented the necessary controls. After that, another security risk assessment was
performed showing that risk has decreased to 10%. The risk threshold for the application is
20%. Which of the following risk decisions will be the best for the project in terms of its
successful continuation with the most business profit?
A.
Accept the risk
B.
Introduce more controls to bring risk to 0%
C.
Mitigate the risk
D.
Avoid the risk
Accept the risk
Explanation:
Risk Mitigation
Risk mitigation can be defined as taking steps to reduce adverse effects. There are four
types of risk mitigation strategies that hold unique to Business Continuity and Disaster
Recovery. When mitigating risk, it’s important to develop a strategy that closely relates to
and matches your company’s profile.
A picture containing diagram
Description automatically generated
Risk Acceptance
Risk acceptance does not reduce any effects; however, it is still considered a strategy. This
strategy is a common option when the cost of other risk management options such as
avoidance or limitation may outweigh the cost of the risk itself. A company that doesn’t
want to spend a lot of money on avoiding risks that do not have a high possibility of
occurring will use the risk acceptance strategy.
Risk Avoidance
Risk avoidance is the opposite of risk acceptance. It is the action that avoids any exposure to the risk whatsoever. It’s important to note that risk avoidance is usually the most
expensive of all risk mitigation options.
Risk Limitation
Risk limitation is the most common risk management strategy used by businesses. This
strategy limits a company’s exposure by taking some action. It is a strategy employing a bit
of risk acceptance and a bit of risk avoidance or an average of both. An example of risk
limitation would be a company accepting that a disk drive may fail and avoiding a long
period of failure by having backups.
Risk Transference
Risk transference is the involvement of handing risk off to a willing third party. For example,
numerous companies outsource certain operations such as customer service, payroll
services, etc. This can be beneficial for a company if a transferred risk is not a core
competency of that company. It can also be used so a company can focus more on its core
competencies.
Which address translation scheme would allow a single public IP address to always
correspond to a single machine on an internal network, allowing "server publishing"?
A.
Overloading Port Address Translation
B.
Dynamic Port Address Translation
C.
Dynamic Network Address Translation
D.
Static Network Address Translation
Static Network Address Translation
The Heartbleed bug was discovered in 2014 and is widely referred to under MITRE’s
Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) as CVE-2014-0160. This bug affects the
OpenSSL implementation of the Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocols defined in
RFC6520.
What type of key does this bug leave exposed to the Internet making exploitation of any
compromised system very easy?
A.
Public
B.
Private
C.
Shared
D.
Root
Private
Which of the following represents the initial two commands that an IRC client sends to join
an IRC network?
A.
USER, NICK
B.
LOGIN, NICK
C.
USER, PASS
D.
LOGIN, USER
USER, NICK
A company’s security policy states that all Web browsers must automatically delete their
HTTP browser cookies upon terminating. What sort of security breach is this policy
attempting to mitigate?
A.
Attempts by attackers to access the user and password information stored in the
company’s SQL database.
B.
Attempts by attackers to access Web sites that trust the Web browser user by stealing
the user’s authentication credentials.
C.
Attempts by attackers to access password stored on the user’s computer without the
user’s knowledge.
D.
Attempts by attackers to determine the user’s Web browser usage patterns, including
when sites were visited and for how long.
Attempts by attackers to access Web sites that trust the Web browser user by stealing
the user’s authentication credentials.
What does a firewall check to prevent particular ports and applications from getting packets
into an organization?
A.
Transport layer port numbers and application layer headers
B.
Presentation layer headers and the session layer port numbers
C.
Network layer headers and the session layer port numbers
D.
Application layer port numbers and the transport layer headers
Transport layer port numbers and application layer headers
Peter, a Network Administrator, has come to you looking for advice on a tool that would
help him perform SNMP enquires over the network.
Which of these tools would do the SNMP enumeration he is looking for? Select the best
answers.
A.
SNMPUtil
B.
SNScan
C.
SNMPScan
D.
Solarwinds IP Network Browser
E.
NMap
SNMPUtil
SNScan
Solarwinds IP Network Browser
Susan has attached to her company's network. She has managed to synchronize her
boss's sessions with that of the file server. She then intercepted his traffic destined for the
server, changed it the way she wanted to and then placed it on the server in his home
directory.
What kind of attack is Susan carrying on?
A.
A sniffing attack
B.
A spoofing attack
C.
A man in the middle attack
D.
A denial of service attack
A man in the middle attack
By using a smart card and pin, you are using a two-factor authentication that satisfies
A.
Something you are and something you remember
B.
Something you have and something you know
C.
Something you know and something you are
D.
Something you have and something you are
Something you have and something you know
Explanation: Two-factor Authentication or 2FA is a user identity verification method, where
two of the three possible authentication factors are combined to grant access to a website
or application.1) something the user knows, 2) something the user has, or 3) something the
user is.
The possible factors of authentication are:
· Something the User Knows:
This is often a password, passphrase, PIN, or secret question. To satisfy this authentication
challenge, the user must provide information that matches the answers previously provided
to the organization by that user, such as “Name the town in which you were born.”
· Something the User Has:
This involves entering a one-time password generated by a hardware authenticator. Users
carry around an authentication device that will generate a one-time password on command.
Users then authenticate by providing this code to the organization. Today, many
organizations offer software authenticators that can be installed on the user’s mobile
device.
· Something the User Is:
This third authentication factor requires the user to authenticate using biometric data. This
can include fingerprint scans, facial scans, behavioral biometrics, and more.
For example: In internet security, the most used factors of authentication are:
something the user has (e.g., a bank card) and something the user knows (e.g., a PIN
code). This is two-factor authentication. Two-factor authentication is also sometimes
referred to as strong authentication, Two-Step Verification, or 2FA.
The key difference between Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) is that, as the term implies, Two-Factor Authentication utilizes a
combination of two out of three possible authentication factors. In contrast, Multi-Factor
Authentication could utilize two or more of these authentication factors.
A network administrator discovers several unknown files in the root directory of his Linux
FTP server. One of the files is a tarball, two are shell script files, and the third is a binary
file is named "nc." The FTP server's access logs show that the anonymous user account
logged in to the server, uploaded the files, and extracted the contents of the tarball and ran
the script using a function provided by the FTP server's software. The “ps” command
shows that the “nc” file is running as process, and the netstat command shows the “nc”
process is listening on a network port.
What kind of vulnerability must be present to make this remote attack possible?
A.
File system permissions
B.
Privilege escalation
C.
Directory traversal
D.
Brute force login
File system permissions
Explanation:
File system permissions
Processes may automatically execute specific binaries as part of their functionality or to
perform other actions. If the permissions on the file system directory containing a target
binary, or permissions on the binary itself, are improperly set, then the target binary may be
overwritten with another binary using user-level permissions and executed by the original
process. If the original process and thread are running under a higher permissions level,
then the replaced binary will also execute under higher-level permissions, which could
include SYSTEM.
Adversaries may use this technique to replace legitimate binaries with malicious ones as a
means of executing code at a higher permissions level. If the executing process is set to
run at a specific time or during a certain event (e.g., system bootup) then this technique
can also be used for persistence.
One of your team members has asked you to analyze the following SOA record.
What is the TTL? Rutgers.edu.SOA NS1.Rutgers.edu ipad.college.edu (200302028 3600
3600 604800 2400.)
A.
200303028
B.
3600
C.
604800
D.
2400
E.
60
F.
4800
2400
Study the following log extract and identify the attack.
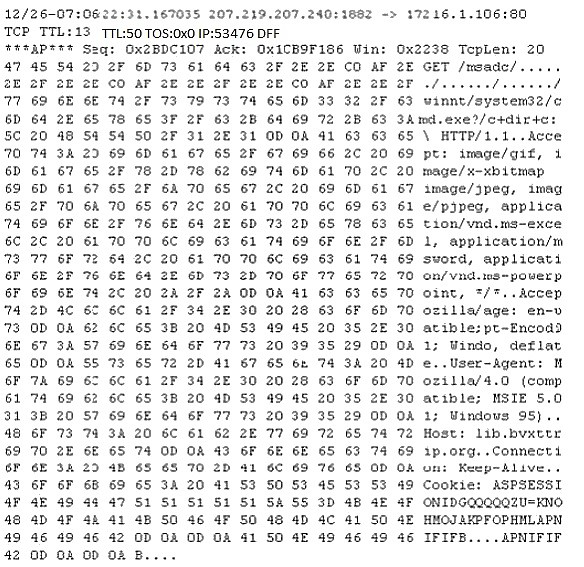
A.
Hexcode Attack
B.
Cross Site Scripting
C.
Multiple Domain Traversal Attack
D.
Unicode Directory Traversal Attack
Unicode Directory Traversal Attack
| Page 9 out of 48 Pages |
| Previous |