Topic 1: Exam Pool A
What tool can crack Windows SMB passwords simply by listening to network traffic?
A.
This is not possible
B.
Netbus
C.
NTFSDOS
D.
L0phtcrack
L0phtcrack
Eve is spending her day scanning the library computers. She notices that Alice is using a
computer whose port 445 is active and listening. Eve uses the ENUM tool to enumerate
Alice machine. From the command prompt, she types the following command.

What is Eve trying to do?
A.
Eve is trying to connect as a user with Administrator privileges
B.
Eve is trying to enumerate all users with Administrative privileges
C.
Eve is trying to carry out a password crack for user Administrator
D.
Eve is trying to escalate privilege of the null user to that of Administrator
Eve is trying to carry out a password crack for user Administrator
What is the way to decide how a packet will move from an untrusted outside host to a
protected inside that is behind a firewall, which permits the hacker to determine which ports
are open and if the packets can pass through the packet-filtering of the firewall?
A.
Session hijacking
B.
Firewalking
C.
Man-in-the middle attack
D.
Network sniffing
Firewalking
When you are getting information about a web server, it is very important to know the
HTTP Methods (GET, POST, HEAD, PUT, DELETE, TRACE) that are available because
there are two critical methods (PUT and DELETE). PUT can upload a file to the server and
DELETE can delete a file from the server. You can detect all these methods (GET, POST,
HEAD, DELETE, PUT, TRACE) using NMAP script engine. What Nmap script will help you
with this task?
A.
http-methods
B.
http enum
C.
http-headers
D.
http-git
http-methods
During a recent security assessment, you discover the organization has one Domain Name
Server (DNS) in a Demilitarized Zone (DMZ) and a second DNS server on the internal
network.
What is this type of DNS configuration commonly called?
A.
DynDNS
B.
DNS Scheme
C.
DNSSEC
D.
Split DNS
Split DNS
Which Intrusion Detection System is the best applicable for large environments where
critical assets on the network need extra scrutiny and is ideal for observing sensitive
network segments?
A.
Honeypots
B.
Firewalls
C.
Network-based intrusion detection system (NIDS)
D.
Host-based intrusion detection system (HIDS)
Network-based intrusion detection system (NIDS)
Which of the following is the BEST way to defend against network sniffing?
A.
Using encryption protocols to secure network communications
B.
Register all machines MAC Address in a Centralized Database
C.
Use Static IP Address
D.
Restrict Physical Access to Server Rooms hosting Critical Servers
Using encryption protocols to secure network communications
Explanation:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sniffing_attack
To prevent networks from sniffing attacks, organizations and individual users should keep
away from applications using insecure protocols, like basic HTTP authentication, File
Transfer Protocol (FTP), and Telnet. Instead, secure protocols such as HTTPS, Secure File
Transfer Protocol (SFTP), and Secure Shell (SSH) should be preferred. In case there is a
necessity for using any insecure protocol in any application, all the data transmission
should be encrypted. If required, VPN (Virtual Private Networks) can be used to provide
secure access to users.
NOTE: I want to note that the wording "best option" is valid only for the EC-Council's exam
since the other options will not help against sniffing or will only help from some specific
attack vectors.
The sniffing attack surface is huge. To protect against it, you will need to implement a
complex of measures at all levels of abstraction and apply controls at the physical,
administrative, and technical levels. However, encryption is indeed the best option of all,
even if your data is intercepted - an attacker cannot understand it.
What did the following commands determine?
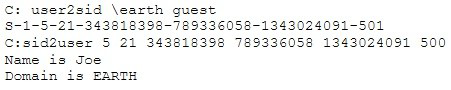
A.
That the Joe account has a SID of 500
B.
These commands demonstrate that the guest account has NOT been disabled
C.
These commands demonstrate that the guest account has been disabled
D.
That the true administrator is Joe
E.
Issued alone, these commands prove nothing
That the true administrator is Joe
Which of the following statements about a zone transfer is correct? (Choose three.)
A.
A zone transfer is accomplished with the DNS
B.
A zone transfer is accomplished with the nslookup service
C.
A zone transfer passes all zone information that a DNS server maintains
D.
A zone transfer passes all zone information that a nslookup server maintains
E.
A zone transfer can be prevented by blocking all inbound TCP port 53 connections
F.
Zone transfers cannot occur on the Internet
A zone transfer is accomplished with the DNS
A zone transfer passes all zone information that a DNS server maintains
A zone transfer can be prevented by blocking all inbound TCP port 53 connections
A zone file consists of which of the following Resource Records (RRs)?
A.
DNS, NS, AXFR, and MX records
B.
DNS, NS, PTR, and MX records
C.
SOA, NS, AXFR, and MX records
D.
SOA, NS, A, and MX records
SOA, NS, A, and MX records
User A is writing a sensitive email message to user B outside the local network. User A has
chosen to use PKI to secure his message and ensure only user B can read the sensitive
email. At what layer of the OSI layer does the encryption and decryption of the message
take place?
A.
Application
B.
Transport
C.
Session
D.
Presentation
Presentation
Explanation: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Presentation_layer
In the seven-layer OSI model of computer networking, the presentation layer is layer 6 and
serves as the data translator for the network. It is sometimes called the syntax layer. The
presentation layer is responsible for the formatting and delivery of information to the
application layer for further processing or display.
Encryption is typically done at this level too, although it can be done on the application,
session, transport, or network layers, each having its own advantages and disadvantages.
Decryption is also handled at the presentation layer. For example, when logging on to bank
account sites the presentation layer will decrypt the data as it is received.
What is a NULL scan?
A.
A scan in which all flags are turned off
B.
A scan in which certain flags are off
C.
A scan in which all flags are on
D.
A scan in which the packet size is set to zero
E.
A scan with an illegal packet size
A scan in which all flags are turned off
| Page 10 out of 48 Pages |
| Previous |