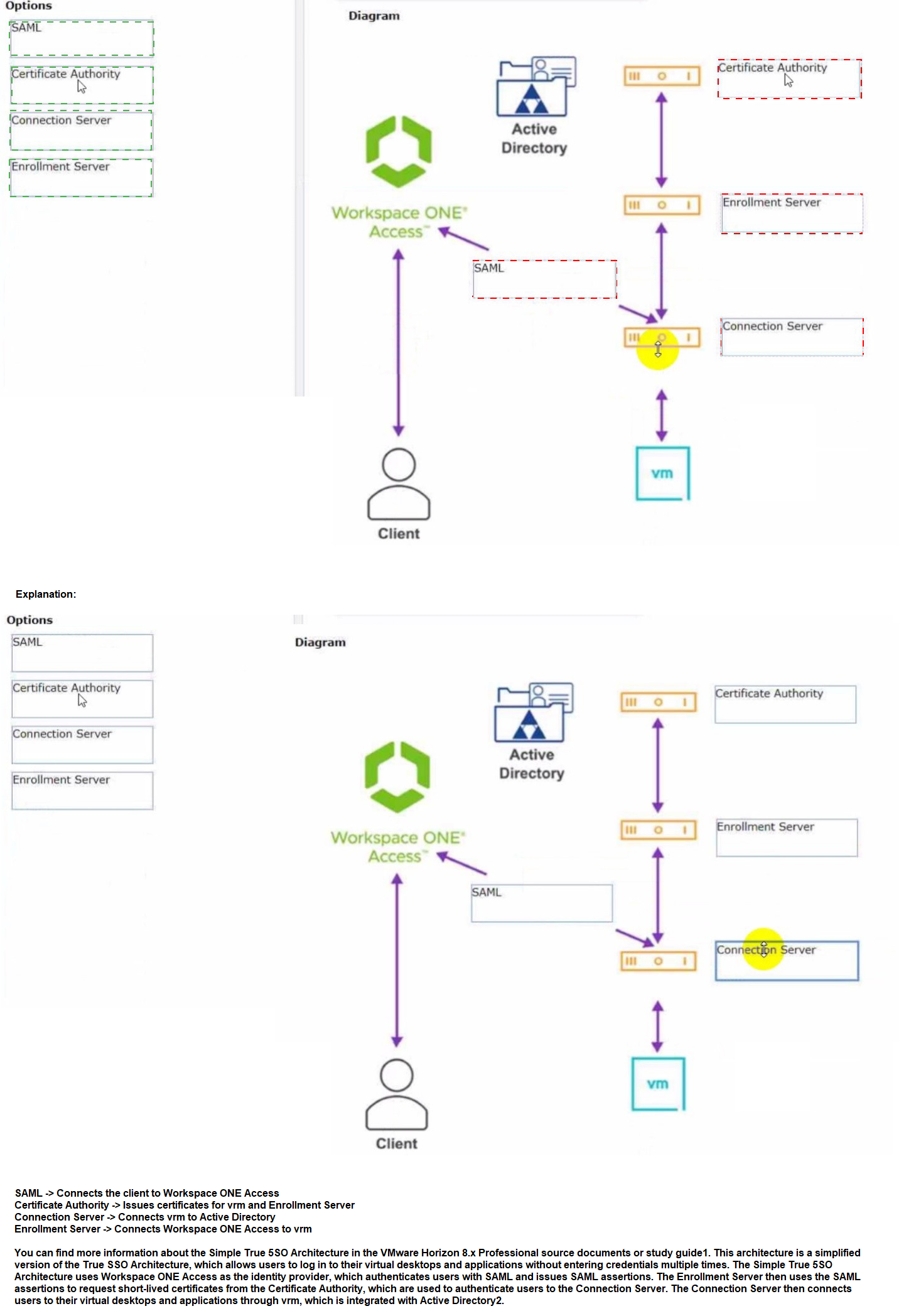
Refer to the exhibit.
Drag and drop the correct options to build a Simple True 5SO Architecture on the left into
the diagram on the right.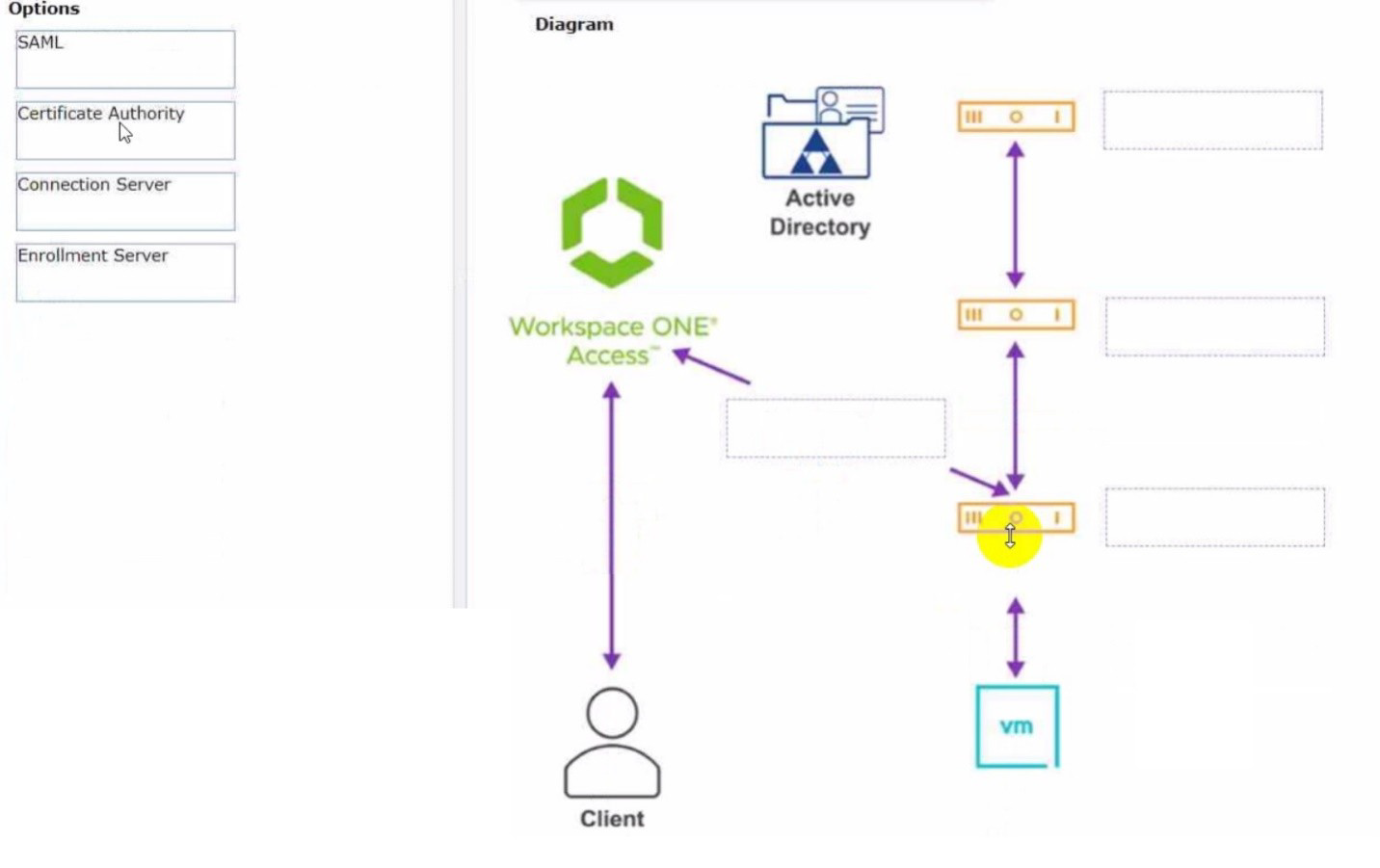
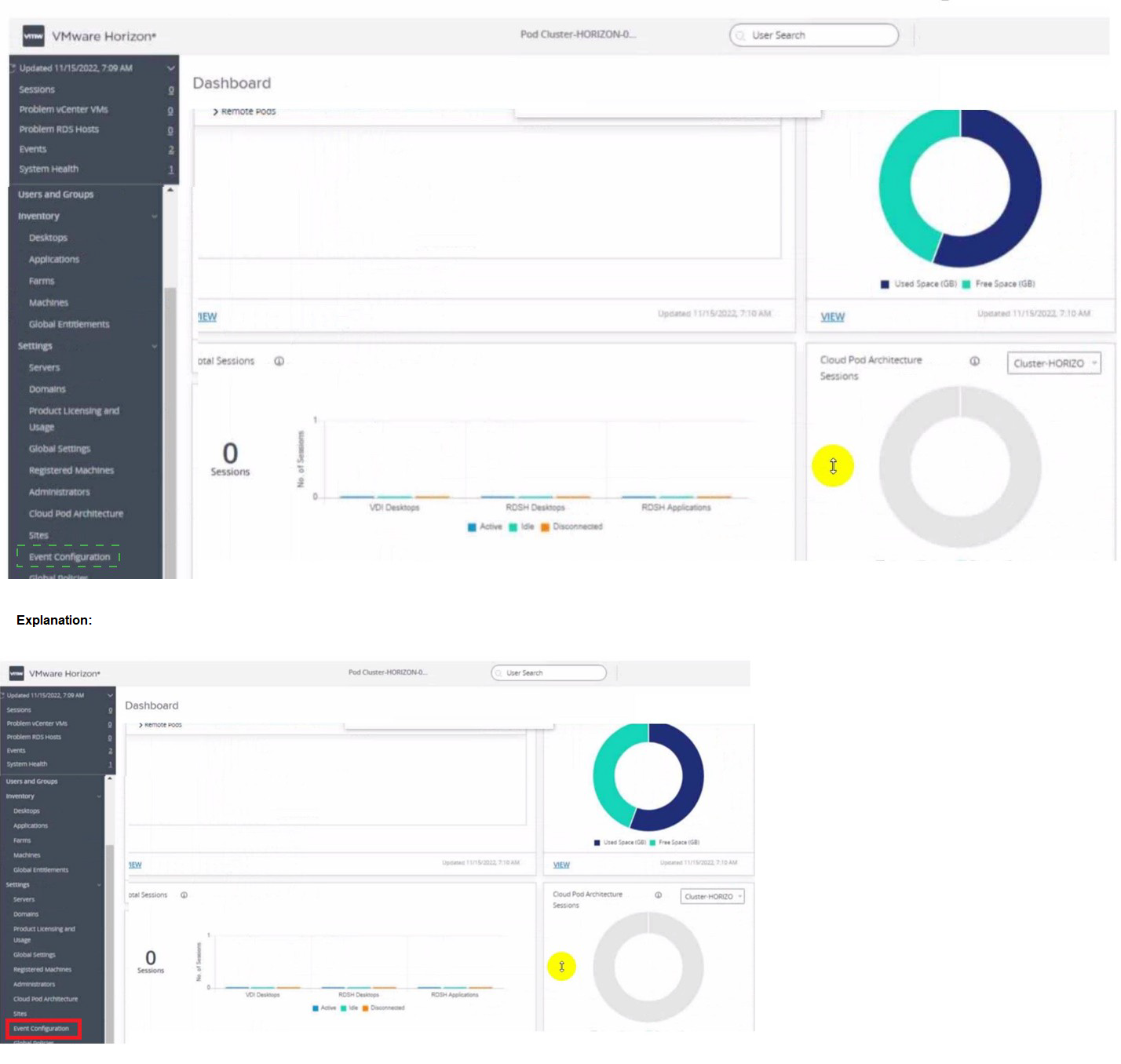
Refer to the exhibit.
An administrator wants to configure a central SYSLOG server.
Mark the correct menu option by clicking on it.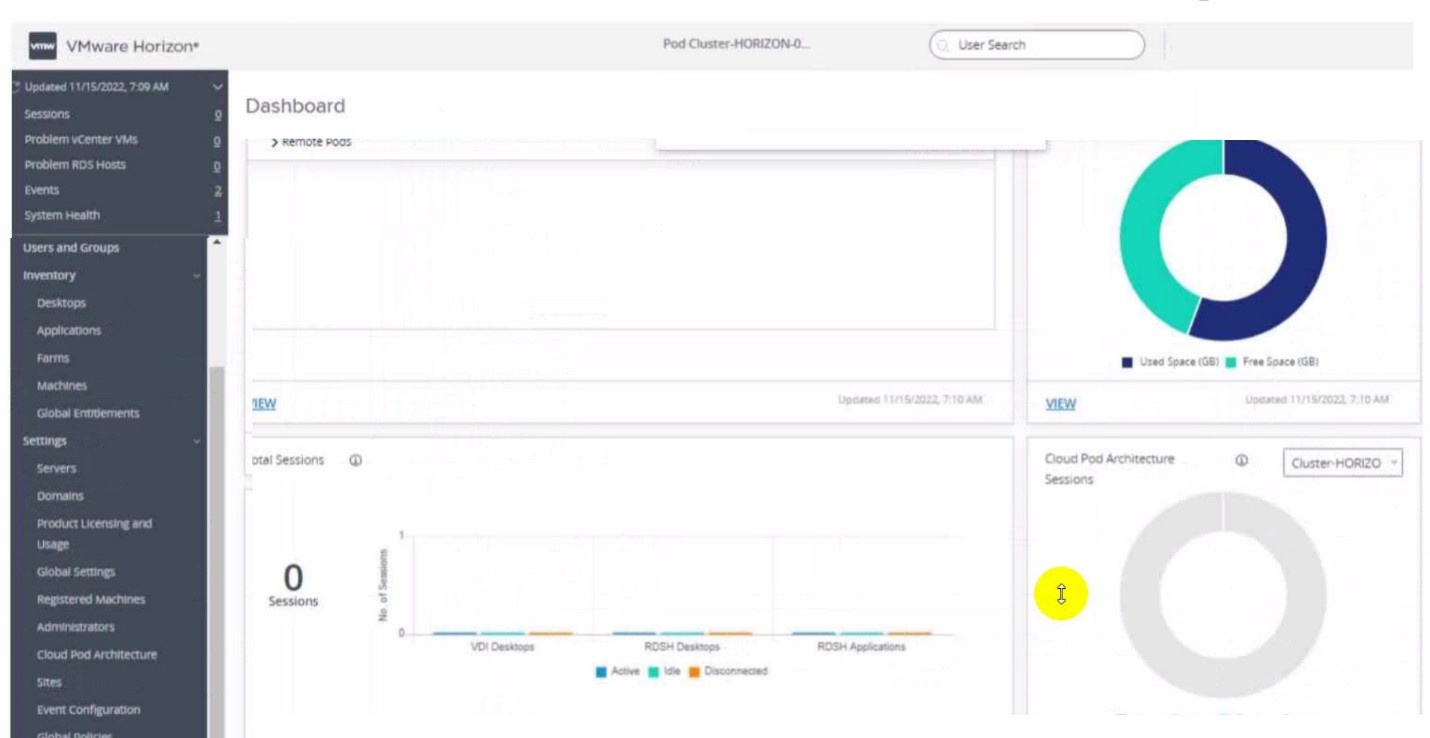
Users need to be able to log into VMware Workspace ONE Access and connect to remote desktops and applications without having to provide Active Directory credentials. Which VMware Horizon component needs to be deployed to allow this functionality?
A. Replica Server
B. Security Server
C. Enrollment Server
D. vCenter Server
Explanation: The VMware Horizon component that needs to be deployed to allow users to
log into VMware Workspace ONE Access and connect to remote desktops and
applications without having to provide Active Directory credentials is the Enrollment
Server. The Enrollment Server is a standalone service that integrates with VMware
Workspace ONE Access and enables True Single Sign-On (SSO) for Horizon clients that
are using non-AD-based authentication methods such as RSA SecureID, RADIUS, or
SAML1. The Enrollment Server requests short-lived certificates on behalf of the users from
a certificate authority (CA), and these certificates are used for authentication to the Horizon
environment2. The Enrollment Server must be installed and configured in the same domain
or forest as the Connection Server, and it must have an enrollment agent certificate that
authorizes it to act as an enrollment agent2.
The other options are not valid or feasible because:
A Replica Server is a Connection Server instance that replicates the Horizon
LDAP configuration data from another Connection Server instance, and provides
high availability and load balancing for user connections3. A Replica Server does
not request or issue certificates for users, and it does not integrate with VMware
Workspace ONE Access.
A Security Server is a Connection Server instance that resides within a DMZ and
acts as a proxy for external user connections to the Horizon environment4. A
Security Server does not request or issue certificates for users, and it does not
integrate with VMware Workspace ONE Access. Security Servers are deprecated
in Horizon 8 and replaced by Unified Access Gateways (UAGs)4.
A vCenter Server is a management platform that provides centralized control and
visibility of vSphere hosts and virtual machines in the Horizon environment5. A
vCenter Server does not request or issue certificates for users, and it does not
integrate with VMware Workspace ONE Access.
A junior-level Horizon administrator is not able to see all RDS farms. Where would a high-level administrator need to make changes to correct the issue?
A. Category Folder
B. Access Groups
C. Global Entitlements
D. Global Policies
Explanation: Access groups are a way of organizing and delegating the administration of machines, desktop pools, application pools, and farms in Horizon. By default, all these objects reside in the root access group, which appears as / or Root (/) in Horizon Console. A high-level administrator can create sub-access groups under the root access group and assign different permissions to different administrators for each access group. For example, a high-level administrator can create an access group called RDS Farms and assign the Inventory Administrators role to a junior-level administrator for that access group. This way, the junior-level administrator can see and manage all the RDS farms that are in the RDS Farms access group, but not the ones that are in other access groups or the root access group. Therefore, to correct the issue of a junior-level administrator not being able to see all RDS farms, a high-level administrator needs to make changes to the access groups and the permissions associated with them.
The administrator of Windows 10 desktops in a VMware Horizon environment needs to
build a new Windows 10 desktop pool. This new pool will be dedicated to training and
onboarding new employees. The administrator has created a shortcut on a test machine,
which has successfully opened the web browser to the on-boarding applications. After
deploying the new desktop pool across the company, the administrator notices that the
shortcut placed on desktops is not available to any other user connecting to the desktop
pool.
Which two options are available for the administrator to make this shortcut available to all
desktop pool users, while minimizing ongoing administrative effort, before updating the
desktop pool golden image? (Choose two.)
A. Copy the shortcut during user provisioning to a non-writeable App Volume.
B. Copy the shortcut to the Windows Default Domain Controller Policy.
C. Copy the shortcut to c:\users\Public\Desktop.
D. Configure a Shortcut with Horizon View Client.
E. Configure a Shortcut with DEM (Dynamic Environment Manager).
Explanation: The two options that are available for the administrator to make the shortcut
available to all desktop pool users, while minimizing ongoing administrative effort, before
updating the desktop pool golden image are:
Copy the shortcut to c:\users\Public\Desktop. This option will place the shortcut in
the public desktop folder, which is shared by all users who log on to the same
computer. The public desktop folder is normally a hidden folder, so the
administrator needs to enable the option to show hidden files and folders in File
Explorer1. This option does not require any additional software or configuration,
but it will only work for the existing desktops in the pool. If new desktops are added
or refreshed, the shortcut will not be copied automatically.
Configure a Shortcut with DEM (Dynamic Environment Manager). This option will
use the DEM console to create a shortcut configuration that will apply the shortcut
to the user’s desktop during logon2. The administrator needs to install and
configure DEM on the Horizon environment, and create a configuration share and
a profile archive share for storing the DEM settings3. This option requires more
initial setup, but it will work for any desktop in the pool, regardless of whether it is
new or refreshed. It also allows more flexibility and control over the shortcut
properties and conditions.
The other options are not valid or feasible because:
Copying the shortcut during user provisioning to a non-writeable App Volume will
not work because App Volumes are used to deliver applications, not
shortcuts. App Volumes are virtual disks that are attached to the virtual machines
at runtime, and they contain application files, registry entries, and settings4.
Copying a shortcut to an App Volume will not make it appear on the user’s
desktop.
Copying the shortcut to the Windows Default Domain Controller Policy will not
work because this policy is used to configure settings for domain controllers, not
desktops. The Default Domain Controller Policy is a Group Policy Object (GPO)
that is linked to the Domain Controllers organizational unit (OU) in Active Directory,
and it contains security settings that are applied to all domain controllers in the
domain5. Copying a shortcut to this policy will not affect any desktops in the
Horizon environment.
Configuring a Shortcut with Horizon View Client will not work because Horizon
View Client is used to connect to remote desktops and applications, not to create
shortcuts. Horizon View Client is a software application that runs on various
devices and platforms, and it allows users to access their virtual desktops and
applications through a secure connection6. Configuring a shortcut with Horizon
View Client will not make it appear on the user’s desktop.
In a load balanced Horizon POD with three Connection Servers, there are 450 active Blast sessions connected. What happens if one of these Connection Servers runs into an unplanned outage?
A. All 450 active sessions are disconnected, and have to re-connect again by the end-user.
B. All active sessions will stay connected, because HTTPS Secure Tunnel and Blast Secure Gateway are disabled.
C. All 450 active session are logged off immediately.
D. Only the active sessions from the failed Connection Server are disconnected, because HTTPS Secure Tunnel is disabled.
Explanation:
In a load balanced Horizon POD with three Connection Servers, there are 450 active Blast
sessions connected. If one of these Connection Servers runs into an unplanned outage,
only the active sessions from the failed Connection Server are disconnected, because
HTTPS Secure Tunnel is disabled. This means that the other two Connection Servers can
still handle the remaining sessions without interruption.
The HTTPS Secure Tunnel is a feature that allows Horizon Client devices to establish
secure connections to virtual desktops and applications through the Connection Server.
When this feature is enabled, all the display protocol traffic is tunneled through the
Connection Server, which acts as a proxy between the client and the desktop. This
increases the security and simplifies the network configuration, but also adds some
overhead and dependency on the Connection Server availability1.
When this feature is disabled, the Horizon Client devices connect directly to the desktops
using their IP addresses or hostnames, bypassing the Connection Server. This reduces the
load and dependency on the Connection Server, but also requires more network
configuration and firewall rules to allow direct access to the desktops2.
The Blast Secure Gateway is a similar feature that allows Horizon Client devices to
establish secure connections to virtual desktops and applications using the Blast Extreme
protocol through the Connection Server. When this feature is enabled, the Blast Extreme
traffic is tunneled through the Connection Server, which acts as a gateway between the
client and the desktop. When this feature is disabled, the Horizon Client devices connect
directly to the desktops using Blast Extreme3.
In this scenario, both HTTPS Secure Tunnel and Blast Secure Gateway are disabled,
which means that the Horizon Client devices connect directly to the desktops using Blast
Extreme. Therefore, if one of the Connection Servers fails, only the sessions that were
authenticated by that Connection Server are affected. The other sessions can continue
without interruption, as long as they can reach their desktops directly4.
The other options are not correct for this scenario:
Which vCenter privileges are required only for instant clones VMs with a Trusted Platform Module (vTPM) device?
A. Upgrade virtual machine compatibility
B. Manage KM5
C. Configure Host USB device
D. Manage custom attributes
Explanation: A Trusted Platform Module (vTPM) is a virtualized version of a physical TPM
device that provides enhanced security for virtual machines. A vTPM device can be added
to a virtual machine to enable features such as encryption, attestation, and key
management. A vTPM device requires a Key Management Server (KMS) to store and
manage the encryption keys.
To create instant clones VMs with a vTPM device, the vCenter Server user must have
certain privileges in addition to those required for instant clones without a vTPM device.
One of these privileges is Manage KMS, which allows the user to perform cryptographic
operations on the vTPM device, such as cloning, decrypting, encrypting, migrating, and
registering. The Manage KMS privilege is part of the Cryptographic operations privilege
group on vCenter Server.
The other options are not required only for instant clones VMs with a vTPM device:
Which pre-requisite should be met before installing the Horizon Connection Server?
A. The host system must be a vSphere VM with a static IP address.
B. Use a domain user account with administrator privileges on the Horizon Connection Server.
C. An SSL server certificate must be installed on the Horizon Connection Server.
D. Install AD DS and AD LDS Tools on the Horizon Connection Server.
Explanation: One of the prerequisites for installing the Horizon Connection Server is to use a domain user account with administrator privileges on the system. This is because the installer needs to access and modify certain system files and registry settings, as well as create and configure the VMware Horizon View services. The installer also authorizes an Administrators account that has full administration rights for the Horizon environment, including the right to install replicated Connection Server instances. The other options are not prerequisites for installing the Horizon Connection Server. The host system can be a physical or virtual machine, but it must have an IP address that does not change. An SSL server certificate is not required for the initial installation, but it is recommended to replace the default self-signed certificate with a valid certificate from a trusted CA after the installation. AD DS and AD LDS Tools are not required for installing the Horizon Connection Server, but they can be useful for troubleshooting and managing the ADAMdatabase that stores the Horizon configuration data.
On a VMware vCenter managed virtual machine, how does the VMware Horizon Agent know which Connection Server it should register with during the Instant Clone pool creation process?
A. Administrator provides this information in the "Add Pool" creation wizard.
B. Horizon Agent retrieves this information from an DNS SRV record.
C. Administrator provides this information in the Horizon Agent Installation Wizard on the master image.
D. Horizon Agent queries VMware Tools for a Guestlnfo Variable during the cloning process.
Explanation:
On a VMware vCenter managed virtual machine, the VMware Horizon Agent
knows which Connection Server it should register with during the Instant Clone pool
creation process by querying VMware Tools for a Guestlnfo Variable during the cloning
process. The Guestlnfo Variable is a custom property that is set on the parent virtual
machine and contains the FQDN of the Connection Server. When the parent virtual
machine is cloned, the Guestlnfo Variable is copied to the clone and read by the Horizon
Agent. The Horizon Agent then registers with the Connection Server specified in the
Guestlnfo Variable12.
The other options are not correct for this scenario:
An administrator is configuring load-balancing settings in Horizon Console for a RDSH Farm. Which two check boxes can be selected to influence the load balancing behavior? (Choose two.)
A. The floating dynamic host profile setting, created in the vSphere profile section.
B. The use custom script setting for customized RDSH load balancing.
C. The Include Session Count setting to include the session count on the RDSH for load balancing.
D. The Horizon DRS setting for fully automated vSphere load balancing.
Explanation:
Load balancing is a feature that allows administrators to distribute the load of
published desktop and application sessions across multiple RDS hosts in a farm. Load
balancing can improve the performance and availability of the sessions and the hosts.
Horizon offers two ways of configuring load balancing for RDS hosts: using load balancing
settings in Horizon Console or using custom load balancing scripts.
The load balancing settings in Horizon Console allow administrators to define how Horizon
calculates the server load index, which indicates the load on each RDS host. The server
load index can range from 0 to 100, where 0 represents no load and 100 represents full
load. A server load index of -1 indicates that load balancing is disabled. Horizon uses the
server load index to determine which RDS host is the best candidate for placing a new
session request.
The load balancing settings in Horizon Console include the following check boxes that can
be selected to influence the load balancing behavior:
Refer to the exhibit.
An administrator wants to set the initial login into a VDI desktop to be full screen.
In the Group Policy Management Editor Window, mark the setting that needs to be
configured by clicking on it.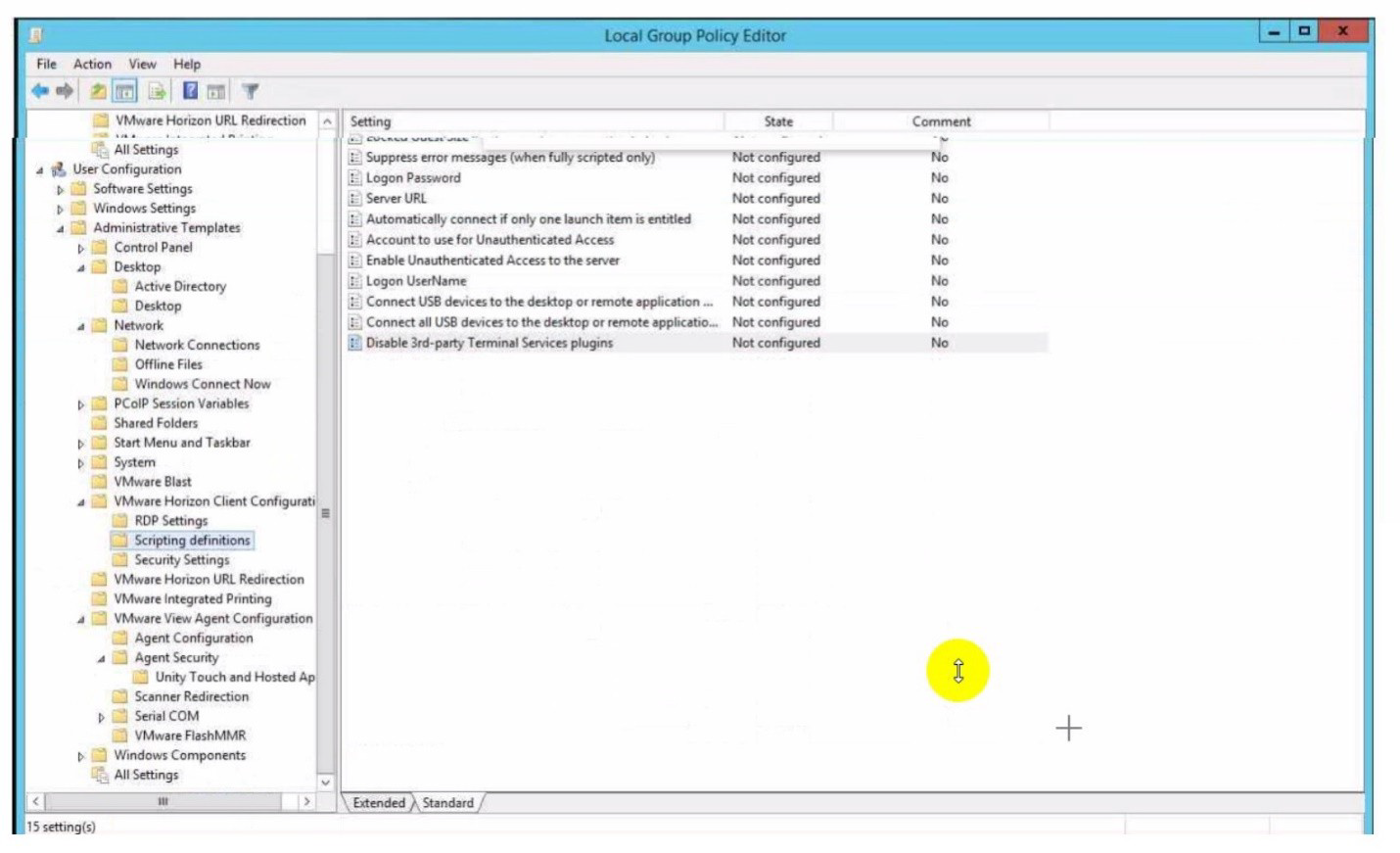
How do multiple Horizon Connection Server instances in a pod maintain synchronization?
A. Horizon Connection Server instances keep their data in an AD LDS database, which is automatically synchronized between the Connection Server.
B. Horizon Connection Server instances keep their data in an Oracle database, which works as the central hub.
C. Horizon Connection Server instances keep their data in a local MySQL DB. The data is synchronized once every 24h.
D. Horizon Connection Server instances keep their data in an MS SQL database, which works as the central hub.
Explanation: Horizon Connection Server instances keep their data in an AD LDS database, which is automatically synchronized between the Connection Server. AD LDS is a Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) directory service that provides flexible support for directory-enabled applications, without the dependencies that are required for Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS). AD LDS provides much of the same functionality as AD DS, but it does not require the deployment of domains or domain controllers. In a Horizon environment, each Connection Server instance has a copy of the AD LDS database and replicates changes to other Connection Server instances in the same pod. This ensures that the Connection Server instances have consistent and up-to-date information about the Horizon resources and user sessions.
| Page 1 out of 8 Pages |