Topic 2, Exam B
R1 has learned route 10.10.10.0/24 via numerous routing protocols. Which route is installed?
A.
route with the lowest cost
B.
route with the next hop that has the highest IP
C.
route with the shortest prefix length
D.
route with the lowest administrative distance
route with the lowest administrative distance
Refer to the exhibit.
If configuring a static default route on the router with the ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.13.0.1
120 command how does the router respond?
A.
It ignores the new static route until the existing OSPF default route is removed
B.
It immediately replaces the existing OSPF route in the routing table with the newly configured static route
C.
It starts load-balancing traffic between the two default routes
D.
It starts sending traffic without a specific matching entry in the routing table to
GigabitEthernetO/1
It ignores the new static route until the existing OSPF default route is removed
Explanation: Our new static default route has the Administrative Distance (AD) of 120,
which is bigger than the AD of OSPF External route (O*E2) so it will not be pushed into the
routing table until the current OSPF External route is removed.For your information, if you
don’t type the AD of 120 (using the command “ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.13.0.1”) then the
new static default route would replace the OSPF default route as the default AD of static
route is 1. You will see such line in the routing table:S* 0.0.0.0/0 [1/0] via 10.13.0.1
What is the benefit of configuring PortFast on an interface?
A.
After the cable is connected, the interface uses the fastest speed setting available for
that cable type
B.
After the cable is connected, the interface is available faster to send and receive user data
C.
The frames entering the interface are marked with higher priority and then processed faster by a switch.
D.
Real-time voice and video frames entering the interface are processed faster
After the cable is connected, the interface is available faster to send and receive user data
How do traditional campus device management and Cisco DNA Center device
management differ in regards to deployment?
A.
Cisco DNA Center device management can deploy a network more quickly than
traditional campus device management
B.
Traditional campus device management allows a network to scale more quickly than
with Cisco DNA Center device management
C.
Cisco DNA Center device management can be implemented at a lower cost than most
traditional campus device management options
D.
Traditional campus device management schemes can typically deploy patches and
updates more quickly than Cisco DNA Center device management
Cisco DNA Center device management can deploy a network more quickly than
traditional campus device management
Drag and drop the descriptions from the left onto the configuration-management
technologies on the right.


Refer to the exhibit.
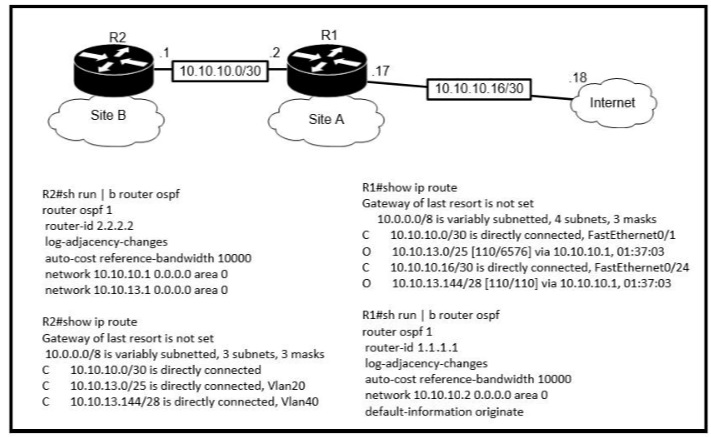
An engineer is bringing up a new circuit to the MPLS provider on the Gi0/1 interface of
Router1 The new circuit uses eBGP and teams the route to VLAN25 from the BGP path
What s the expected behavior for the traffic flow for route 10.10.13.0/25?
A.
Traffic to 10.10.13.0.25 is load balanced out of multiple interfaces
B.
Route 10.10.13.0/25 is updated in the routing table as being learned from interface
Gi0/1.
C.
Traffic to 10.10.13.0/25 is asymmeteical
D.
Route 10.10.13.0/25 learned via the GiO/0 interface remains in the routing table
Route 10.10.13.0/25 learned via the GiO/0 interface remains in the routing table
What is a function of TFTP in network operations?
A.
transfers a backup configuration file from a server to a switch using a username and password
B.
transfers files between file systems on a router
C.
transfers a configuration files from a server to a router on a congested link
D.
transfers IOS images from a server to a router for firmware upgrades
transfers IOS images from a server to a router for firmware upgrades
Explanation: TFTP is mostly used (Firmware upgrade) whereby the admin have the IOS
image on one device and uses TFTP to load the image to all other devices quickly.
Refer to the exhibit.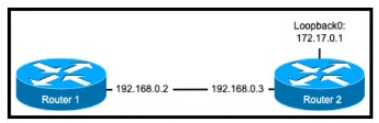
The nip server 192.168.0.3 command has been configured on router 1 to make it an NTP
client of router 2. Which command must be configured on router 2 so that it operates in
server-only mode and relies only on its internal clock?
A.
Router2(config)#ntp passive
B.
Router2(config)#ntp server 172.17.0.1
C.
Router2(config)#ntp master 4
D.
Router2(config)#ntp server 192.168.0.2
Router2(config)#ntp server 172.17.0.1
Explanation: • To use internal clock of this router, use any configured IP address in any
interface of this router.
Refer to the exhibit.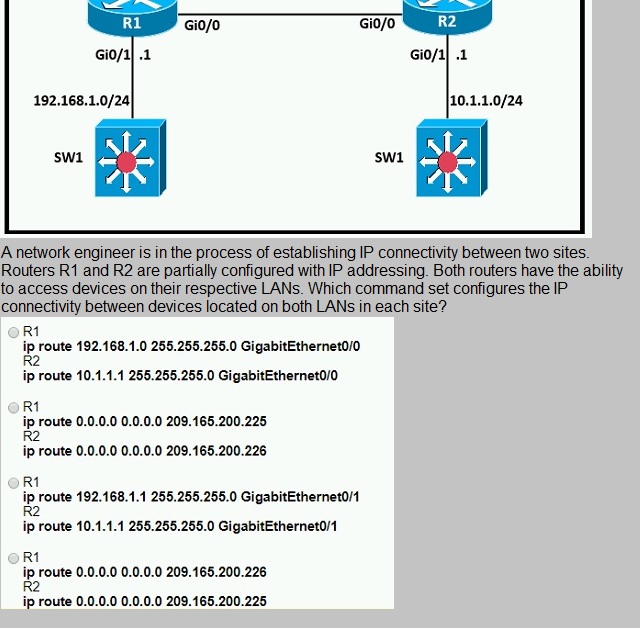
A.
Option A
B.
Option B
C.
Option C
D.
Option D
Option D
Which action must be taken to assign a global unicast IPv6 address on an interface that is derived from the MAC address of that interface?
A.
configure a stateful DHCPv6 server on the network
B.
enable SLAAC on an interface
C.
disable the EUI-64 bit process
D.
explicitly assign a link-local address
enable SLAAC on an interface
Refer to me exhibit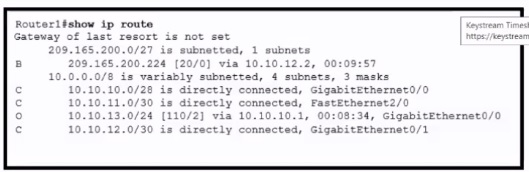
Which action is taken by the router when a packet is sourced from 10.10.10.2 and destined
for 10.10.10.16?
A.
It uses a route that is similar to the destination address
B.
It discards the packets.
C.
It floods packets to all learned next hops.
D.
It Queues the packets waiting for the route to be learned.
It uses a route that is similar to the destination address
Which goal is achieved by the implementation of private IPv4 addressing on a network?
A.
provides an added level of protection against Internet exposure
B.
provides a reduction in size of the forwarding table on network routers
C.
allows communication across the Internet to other private networks
D.
allows servers and workstations to communicate across public network boundaries
provides an added level of protection against Internet exposure
| Page 23 out of 72 Pages |
| Previous |