Which three are true about Oracle Grid Infrastructure for a Standalone Server?
A.
It includes both Oracle Restart and OracleAutomatic Storage Management (ASM) software.
B.
It creates one disk group during installation.
C.
It requires the operating system oracle_base environment variable to be predefined before installation
D.
It requires Oracle ASM Filter Driver (ASMFD) to manage Automatic Storage Management (ASM)
disks
E.
It requires Oracle ASMLibto manage Automatic Storage Management (ASM) disks.
F.
Automatic Storage Management (ASM) requires that O/S groups OSASM and OSDBA be assigned as
secondary groups for its installationowner.
It includes both Oracle Restart and OracleAutomatic Storage Management (ASM) software.
It creates one disk group during installation.
It requires Oracle ASM Filter Driver (ASMFD) to manage Automatic Storage Management (ASM)
disks
Examine this configuration:
1.The ORCL database data files are in Automatic Storage Management (Oracle ASM) disk group +DATA.
2.ORCL uses disk group +FRAfor the Fast Recovery Area.
3.LISTENER is the listener for ORCL.
4.The database, listener, ASM instance, and ASM disk groups are managed by Oracle Restart.
5.All components are currently shut down.
You execute this command:
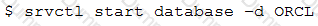
What is the outcome?
A.
The ORCL database, the Oracle ASM instances, the +DATA and +FRA disk groups, and the
LISTENER
are started.
B.
Only the ORCL database instance is started.
C.
Only the ORCL database and the ASM instances are started
D.
Only the ORCL database instance, the Oracle ASM instance, and the +DATA and +FRA disk groups
are started.
E.
Only the ORCL database instance and the +DATA and +FRA disk groups are started.
Only the ORCL database instance, the Oracle ASM instance, and the +DATA and +FRA disk groups
are started.
Which two are true about Rapid Home Provisioning (RHP), which has been available since Orcale 18c?
(Choose two.)
A.
It is an Oracle Database service
B.
It cannot be usedto upgrade Oracle Database homes.
C.
It can be used to provision applications
D.
It can be used to patch Grid Infrastructure homes containing Oracle Restart.
E.
It can be used to provision middleware.
It can be used to patch Grid Infrastructure homes containing Oracle Restart.
It can be used to provision middleware.
Which three are true about upgrading Oracle Grid Infrastructure? (Choose three.)
A.
A direct upgrade can be performed only from the immediately preceding Oracle Grid Infrastructure
version.
B.
The newer version is installed in a separate Oracle Grid Infrastructure home on the same server as the
existing version
C.
An existing Oracle base can be used.
D.
The upgrade process will automatically install all mandatory patches for the current version of Oracle
Grid Infrastructure.
E.
Existing Oracle Database instances must be shut down before starting the upgrade.
F.
Only the grid user can perform the upgrade.
The upgrade process will automatically install all mandatory patches for the current version of Oracle
Grid Infrastructure.
Existing Oracle Database instances must be shut down before starting the upgrade.
Only the grid user can perform the upgrade.
Which three are true about Recovery Manager (RMAN) in Oracle Database 19c and later releases? (Choose three.)
A.
It is only possible for RMAN to connect to a pluggable database as a target if an RMAN Virtual Private
Catalog is used.
B.
It isalways possible for RMAN to connect to a pluggable database as a target if any RMAN Catalog is
used.
C.
A Virtual Private Catalog used to register a container database must be created in a pluggable database.
D.
A Virtual Private Catalog used to registera container database can be created in a pluggable database.
E.
It is always possible for RMAN to connect to a pluggable database as a target.
F.
A Virtual Private Catalog used to register a container database can be created in a non-container
database.
A Virtual Private Catalog used to registera container database can be created in a pluggable database.
It is always possible for RMAN to connect to a pluggable database as a target.
A Virtual Private Catalog used to register a container database can be created in a non-container
database.
Which three are true about managing memory components in an Oracle database instance? (Choose three.)
A.
With Automatic Shared Memory Management, the database instance can increase the Large Pool size
byreducing the Shared Pool size
B.
With Automatic Memory Management, the database instance can increase the System Global Area size
by reducing the Program Global Area size.
C.
Automatically tuned and resized System Global Area components will always revertto their initial sizes
after an instance restart.
D.
Automatic Memory Management must be used together with locking the System Global Area into physical memory.
E.
With Automatic Shared Memory Management, the database instance can increase the Program Global
Area size by reducing the System Global Area size.
F.
On Line Transaction Processing systems often use less Program Global Area than Decision Support
Systems.
With Automatic Shared Memory Management, the database instance can increase the Large Pool size
byreducing the Shared Pool size
With Automatic Shared Memory Management, the database instance can increase the Program Global
Area size by reducing the System Global Area size.
On Line Transaction Processing systems often use less Program Global Area than Decision Support
Systems.
Examine this configuration:
CDB1is a container database.
PDB1andPDB2are pluggable databases inCDB1.
You execute these commands successfully:

Which two are true? (Choose two.)
A.
PDB1 and PDB2 are in MOUNT state
B.
Redo logs are opened.
C.
PDB1 and PDB2 are in READ ONLY state
D.
CDB$ROOT is in MOUNT state.
E.
PDB$SEED is in READ ONLY state.
Redo logs are opened.
PDB$SEED is in READ ONLY state.
Which two are true about Oracle instance recovery? (Choose three.)
A.
Recovery begins from the beginning of the CURRENT redo log group.
B.
Recovery begins from the last checkpoint position that wascalculated by the Database Writer before
instance failure.
C.
Recovery begins from the start of any ACTIVE redo log group or the start of the CURRENT log group
if no other group is ACTIVE.
D.
Recovery reads redo until the end of the redo thread. SMON rollsback any dead transactions, and then
the datanase is opened.
E.
Recovery begins from the last checkpoint position that was recorded in the control file by the checkpoint
process (CKPT).
F.
Recovery reads redo until the end of the redo thread, and then opens the database. SMON then rolls
back any dead transactions.
Recovery begins from the last checkpoint position that wascalculated by the Database Writer before
instance failure.
Recovery reads redo until the end of the redo thread. SMON rollsback any dead transactions, and then
the datanase is opened.
Recovery reads redo until the end of the redo thread, and then opens the database. SMON then rolls
back any dead transactions.
Which four are true about duplicating a database using Recovery Manager (RMAN)? (Choose four.)
A.
Duplication can be done by having the auxiliary databaseinstance pull backup sets from the target
database instance.
B.
A connection to an auxiliary instance is always required
C.
A subset of the target database can be duplicated.
D.
A new DBID is always created for the duplicated database.
E.
A connection tothe recovery catalog instance is always required.
F.
A backup of the target database is always required.
G.
Duplication can be done by having the target database instance push copies to the auxiliary database
instance.
H.
A connection to the target database instance is always required.
Duplication can be done by having the auxiliary databaseinstance pull backup sets from the target
database instance.
A connection to an auxiliary instance is always required
A backup of the target database is always required.
Duplication can be done by having the target database instance push copies to the auxiliary database
instance.
Which two are true about Oracle Optimizer Statistics, their use, and their collection? (Choose two.)
A.
The number of table rows is considered when evaluating the cost of accessing a table using an index.
B.
Index balanced B*Tree height is considered whenevaluating the cost of using an index
C.
The Statistics Advisor can help recommend the best way to gather statistics.
D.
Statistics collected using DBMS_STATS always yield the best optimizer result.
E.
The Statistics Advisor generates actions for all recommendations.
The Statistics Advisor can help recommend the best way to gather statistics.
Statistics collected using DBMS_STATS always yield the best optimizer result.
Which two are true about server-generated alerts? (Choose two.)
A.
Stateful alerts must be created by a DBA after resolving the problem.
B.
Stateless alerts can be purged manually from the alert history
C.
Stateless alerts can be cleared manually.
D.
Stateless alerts are automatically cleared
E.
Stateful alerts are purged automatically from the alert history.
Stateful alerts must be created by a DBA after resolving the problem.
Stateless alerts can be cleared manually.
Which two are true about the Oracle dataabsemethodology? (Choose two.)
A.
The Oracle Database time model should be used to find the database and instance areas most in need of
tuning.
B.
Tuning activities should stop once the user is satisfied with performance.
C.
Tuning activities should stop onceagreed service levels for performance have been met.
D.
The database instance memory should always be tuned before tuning any file systems.
E.
SQL statements should always be tuned before tuning any file systems.
F.
The alert log should be used to find the database and instance areas most in need of tuning.
Tuning activities should stop onceagreed service levels for performance have been met.
The alert log should be used to find the database and instance areas most in need of tuning.
| Page 3 out of 8 Pages |
| Previous |